Figure 2.
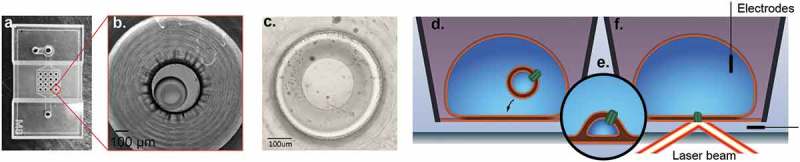
Droplet Hydrogel Bilayers (DHBs). PDMS device (a) with 16 wells is adhered to an agarose-coated size-matched 22 mm × 40 mm coverslip and each well is filled with DPhPC/hexadecane mixture to form a lipid monolayer on the surface. Aqueous droplets consisting of a suspension of proteoliposomes (azolectin liposomes reconstituted with ion channel proteins) are separately incubated in a DPhPC/hexadecane mixture to form a monolayer. The droplet monolayer is then joined with a monolayer on an agarose hydrogel on a glass coverslip to form a bilayer oriented horizontally on a transparent surface (bright field micrograph at low magnification: b; and high magnification: c). Proteoliposomes inside the droplet (d) fuse spontaneously with the bilayer (e) to insert membrane protein, and then an electrode can be inserted in the droplet to record electrical activity whilst simultaneously imaging the bilayer with fluorescence microscopy (f).
