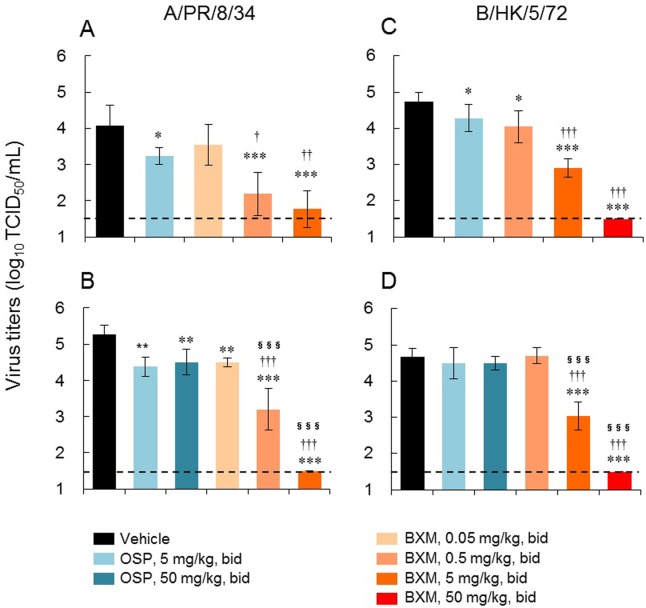
Fig 2. Inhibitory effects of single-day oral administration of BXM on virus titers in lungs in a lethal infection mouse model.
Five mice per group were intranasally infected with (A) 1.38 × 103 or (B) 4.42 × 104 TCID50 virus suspension of A/PR/8/34, or (C) 3.30 × 105 or (D) 1.98 × 106 TCID50 virus suspension of B/HK/5/72 and then orally administered BXM (0.05, 0.5, 5, or 50 mg/kg), OSP (5 or 50 mg/kg), or vehicle bid for 1 day. The virus titers in lungs on day 1 p.i. were measured by TCID50 method. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of 5 mice. The limit of quantification (1.50 log10 TCID50/mL) is indicated by a dotted line. In the A/PR/8/34-infected mouse model, significant differences in virus titers were observed in BXM (except for 0.05 mg/kg bid at the infectious dose of 1.38 × 103 TCID50)- and OSP-treated groups in comparison with the vehicle-treated group (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001). Significant differences in virus titers were also observed between BXM- and OSP-treated groups (†, P < 0.05; ††, P < 0.001; †††, P < 0.0001 vs OSP 5 mg/kg bid; §§§, P < 0.0001 vs OSP 50 mg/kg bid). In the B/HK/5/72-infected mouse model, significant differences in virus titers were observed in BXM (except for 0.5 mg/kg bid at the infectious dose of 1.98 × 106 TCID50)- and OSP (at the infectious dose of 3.30 × 105 TCID50)-treated groups in comparison with the vehicle-treated group (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001). Significant differences in virus titers were also observed between BXM- and OSP-treated groups (†††, P < 0.0001 vs OSP 5 mg/kg bid; §§§, P < 0.0001 vs OSP 50 mg/kg bid).