Figure 1.
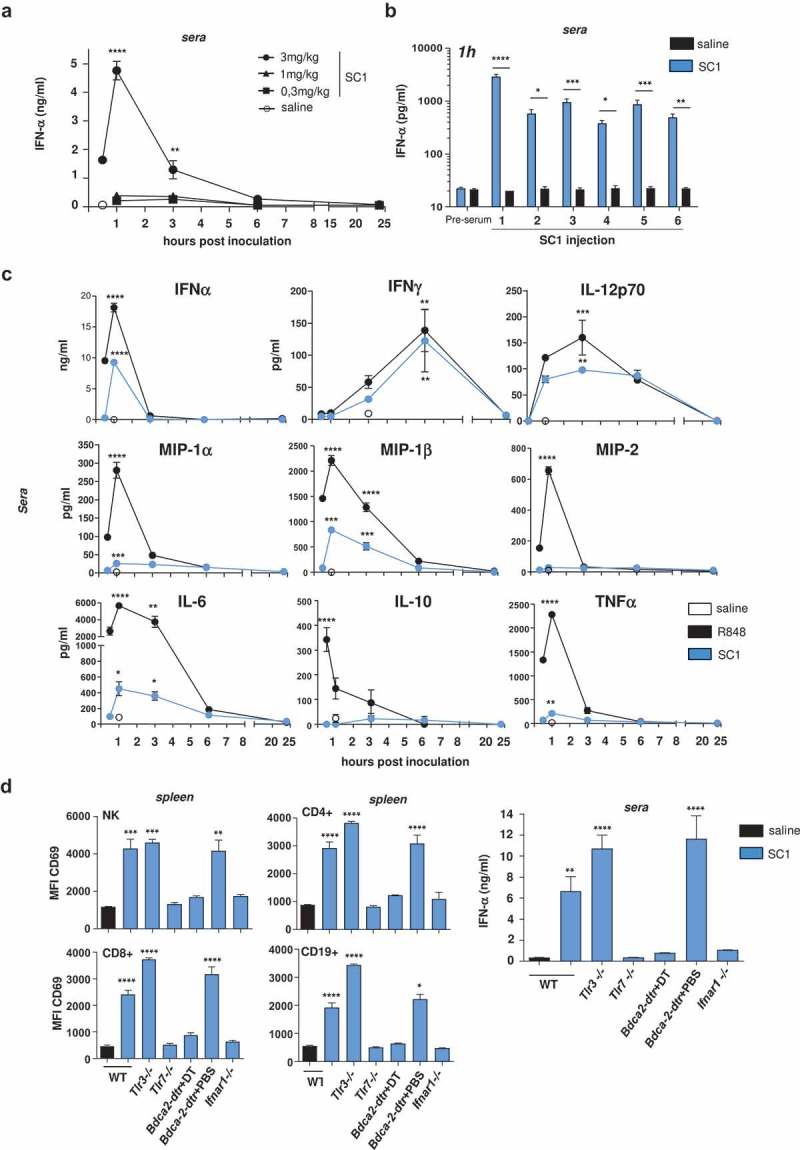
Intravenous administration of SC1 induces TLR7-dependent immune cell activation and IFNα-selective systemic cytokine release.
BALB/c and C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) mice and knock-out variants were injected i.v. with a single or repetitive dose of SC1 (3 mg/kg or as otherwise indicated) or vehicle (saline) every 5 d. (a) Kinetics of IFNα levels in sera of BALB/c WT mice were measured after a single injection of SC1. Data representative of two independent experiments. (b) BALB/c WT mice (n = 3) were given 6 serial i.v. injections of 3 mg/kg SC1 or vehicle (saline) every 5 d. Serum IFNα levels were measured 1 h after each injection. Data representative of two independent experiments. (c) Kinetics of cytokine levels in sera of BALB/c WT mice were measured after a single injection of SC1 or equimolar dose of R848 was measured by Multiplex. (d) CD69 surface expression on different lymphocyte subtypes in the spleen of C57BL/6 WT and knock-out mice 24 h after a single injection of SC1 was measured by flow cytometry (left); IFNα levels in sera 1 h after injection of SC1 was measured by ELISA (right). Data shown as mean ± s.e.m of (a) n = 4–15, (B-D) n = 3–5 mice per group, p*<0.05, p**<0.01, p***<0.001, p****<0.0001 using one-way ANOVA-test using saline as reference group, (c) at the peak of the expression.
