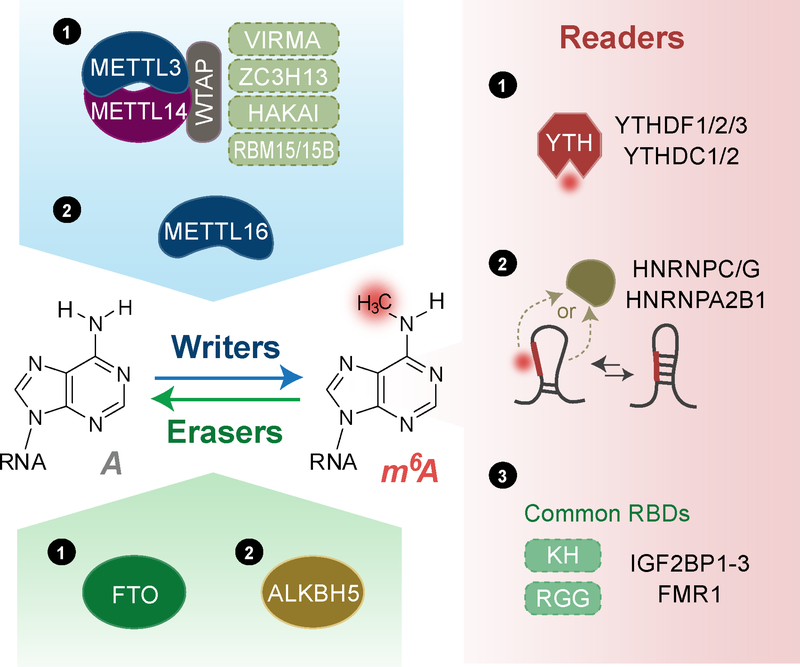
Figure 1. m6A effectors: writers, erasers, and readers.
Writers: Majority of m6A methylation on mRNA is installed by a writer complex ① composed of core subunits METTL3 and METTL14 and additional adaptors proteins including WTAP, VIRMA, ZC3H13, HAKAI, and RBM15/15B in a sequence context of RRACH (R = A or G; H = A, C, or U). The other known writer METTL16 ② installs m6A in a sequence context of UAC(m6A)GAGAA on top of a hairpin structure in transcript MAT2A. Erasers: two erasers have been characterized for m6A methylation on mRNA, including FTO and ALKBH5. Readers: Three classes of reader proteins utilize different mechanisms to prefer binding m6A-containing RNAs. ① YTH-domain containing proteins (YTHDF1–3, YTHDC1–2) use a well-characterized YTH domain to direct recognize m6A methylation. ② A local structure disrupted by the presence of m6A could favor RNA-binding events of HNRNPC/G and HNRNPA2B1. ③ RNA binding proteins including IGF2BP1–3 and FMR1 prefer m6A-containing RNAs through their tandem common RNA binding domains (RBDs) via a mechanism yet to be characterized.