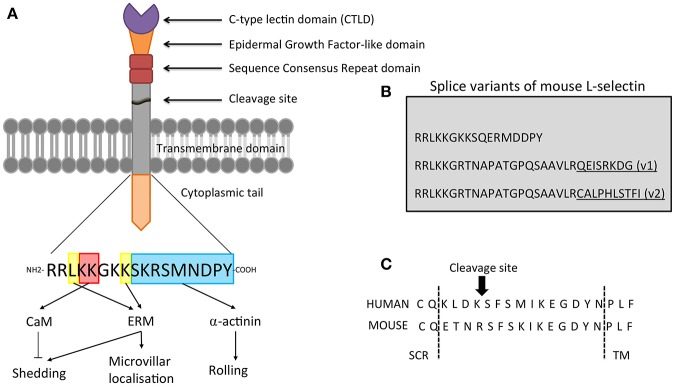
Figure 1.
Domain organization of L-selectin. (A) L-selectin is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein. Going from N-terminal to C-terminal, it is broken down into: C-type lectin domain (CTLD), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-like domain, two sequence consensus repeat (SCR) domains, a cleavage site, transmembrane domain and a 17 amino acid cytoplasmic tail. Amino acid sequence of the cytoplasmic tail of human L-selectin is depicted, highlighting the amino acids that support binding to calmodulin (CaM), ERM proteins, and alpha-actinin. (B) The three sequences correspond to the mouse L-selectin tail (note the mouse L-selectin tail has a single serine at position 364, whereas the tail of human L-selectin possesses an extra serine residue at position 367). Sequence conservation at the membrane-proximal region that support binding to ERM and CaM (RRLKKG) is 100% conserved. The amino acid sequences of two splice variants of mouse L-selectin (v1 and v2) are provided in the sequences below. Underlined residues represent sequences that are unique to v1 and v2. (C) Amino acid sequences surrounding the cleavage site of human and mouse L-selectin. Arrow indicates the position of cleavage. TM, transmembrane domain; SCR, sequence consensus repeat region.