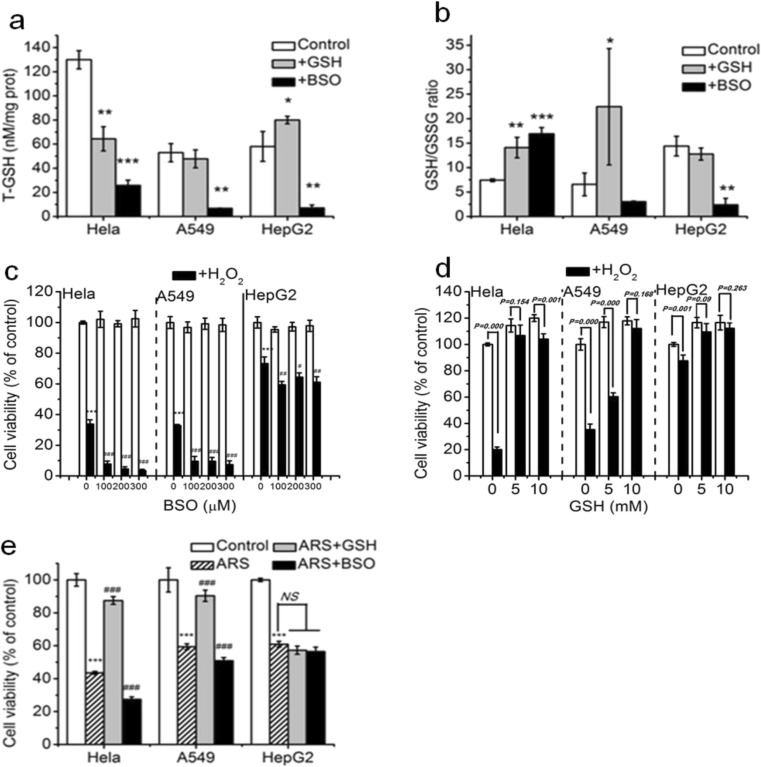
Fig. 3.
Intracellular glutathione plays an important role for the sensitivity of Hela and A549 cell lines to ROS. a and b Intracellular total glutathione (T-GSH) level (a) and GSH/GSSG ratio (b) in the absence or presence of GSH or BSO. Cells were treated with 100 μM BSO for 12 h and 5 mM GSH for 2 h, respectively, and then were detected the intracellular T-GSH level (a) and GSH/GSSG ratio (b) in the three cancer cell lines. c Inhibition of glutathione by BSO markedly enhanced H2O2-induced cytotoxicity in Hela and A549 cell lines but modestly enhanced cytotoxicity of H2O2 in HepG2 cells. d Addition of GSH remarkably prevented H2O2-induced cytotoxicity in Hela and A549 cell lines. Cells were pre-incubated with different concentration of BSO for 12 h (c) and GSH for 2 h (d), respectively, and then treated with H2O2 for 24 h before CCK-8 assay. e GSH played an important role in ARS-induced cytotoxicity in Hela and A549 cell lines but was not involved in ARS-induced cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Cells were pre-incubated with 5 mM GSH and 100 μM BSO, respectively, and then treated with ARS for 48 h. Those results represent duplicates with three independent experiments. NS, no statistical significance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, compared with control; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001, compared with H2O2 or ARS treatment alone