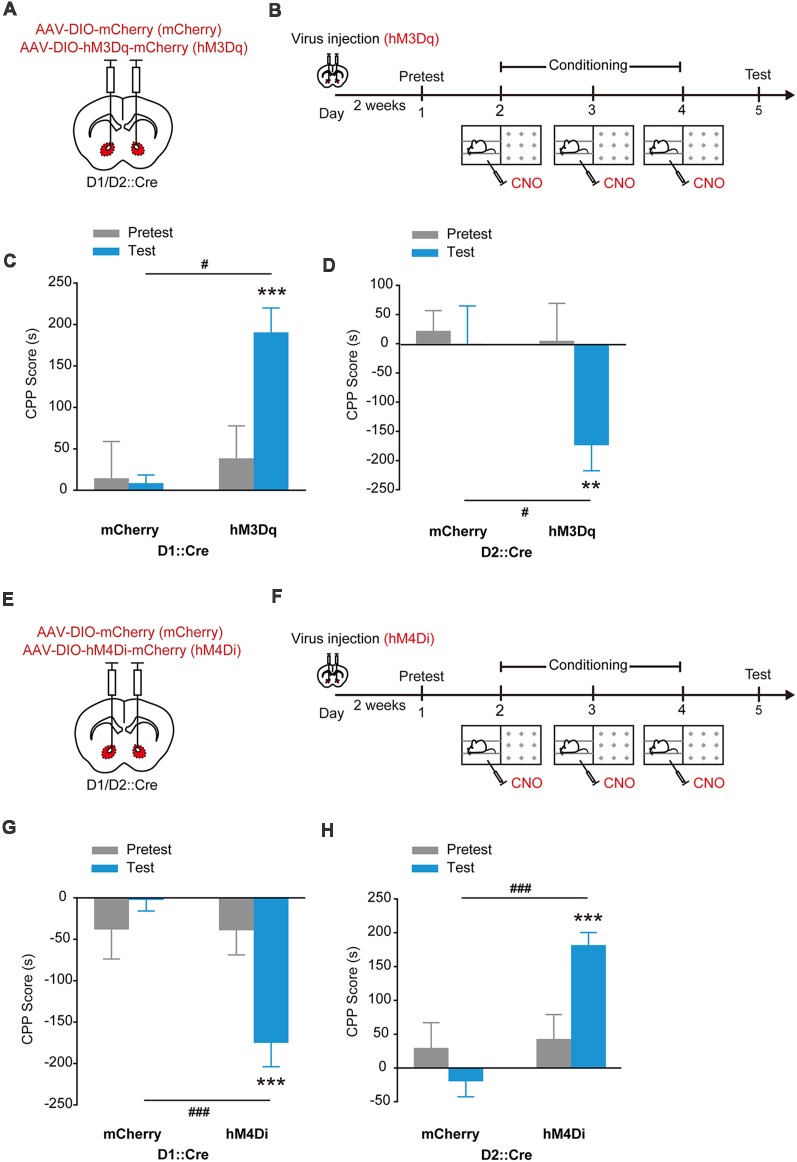
Figure 4.
Chemogenetic activation of hM3Dq or hM4Di in accumbal dSPNs and iSPNs induced opposing emotional valence. (A,B) Virus injection and behavioral scheme. AAV9-EF1α-DIO-mCherry (mCherry) or AAV9-EF1α-DIO-hM3Dq-mCherry (hM3Dq) was infused into the NAcc of D1::Cre and D2::Cre mice. Two to three weeks after surgery, the mice were presented with daily conditioning trials for 3 days: one compartment paired with CNO treatment and the other compartment paired with saline injection. (C,D) Chemogenetic activation of dSPNs promoted CPP formation and activation of iSPNs promoted CPA formation. mCherry, n = 8; D1::Cre, n = 10; D2::Cre, n = 8, ***p < 0.001 vs. Pretest group, #p < 0.05 vs. mCherry group of D1::Cre mice; **p < 0.01 vs. Pretest group, #p < 0.05 vs. mCherry group of D2::Cre mice. (E,F) Virus injection and behavioral scheme. AAV9-EF1α-DIO-mCherry (mCherry) or AAV9-EF1α-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry (hM4Di) was infused into the NAcc of D1::Cre and D2::Cre mice. Two to three weeks after surgery, the mice were presented with daily conditioning trials for 3 days: one compartment paired with CNO treatment and the other compartment paired with saline injection. (G,H) Chemogenetic inhibition of dSPNs promoted CPA formation and inhibition of iSPNs promoted CPP formation. mCherry, n = 11; D1::Cre, n = 11; D2::Cre, n = 12, ***p < 0.001 vs. Pretest group, ###p < 0.001 vs. mCherry group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.