FIGURE 3.
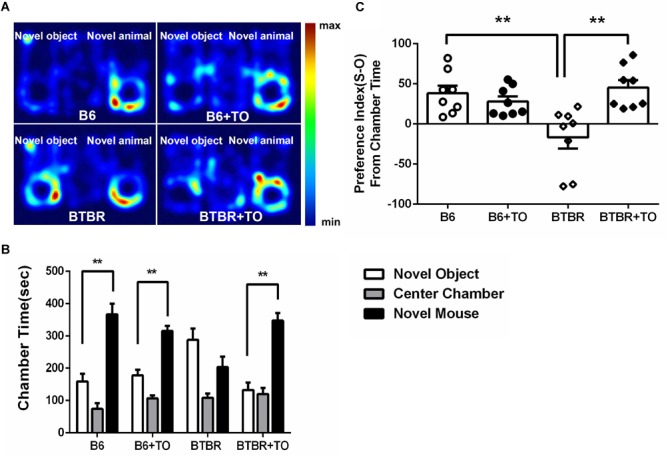
Early postnatal intervention of TO rescued the sociability of BTBR mice. (A) Representative heat maps indicate the time distribution of the experimental mice in the sociability test. Warmer colors (red) represent longer stay. (B) Saline-treated and TO-treated B6 mice spent more time in the chamber with a novel mouse than with a novel object (paired t-test: p < 0.01). BTBR mice displayed impaired sociability and showed a preference toward the novel mouse compared with the novel object. Nevertheless, TO pretreatment reversed the preference significantly (paired t-test: p < 0.01). (C) BTBR mice displayed a lower social preference index (S-O/total) than B6 mice, which could be rescued with TO treatment [two-way ANOVA: drug effect: F(1,28) = 6.616, p < 0.05; genotype effect: F(1,28) = 3.551, p = 0.070; drug x genotype effect: F(1,28) = 12.998, p < 0.01, followed by LSD post hoc test]. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 8. ∗∗p < 0.01.
