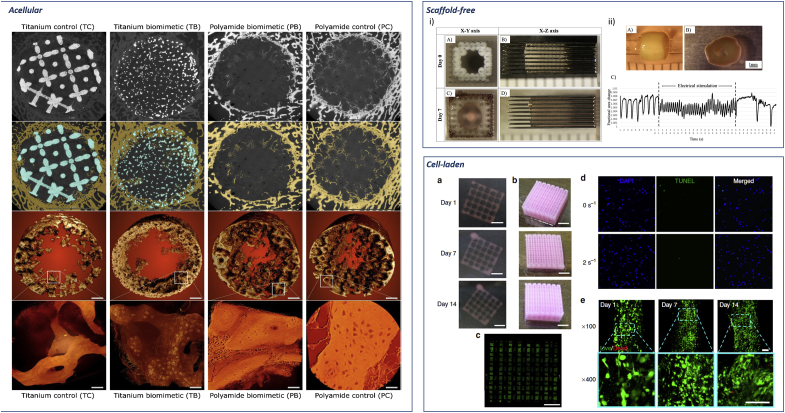
Fig. 3.
Current biofabrication approaches. Acellular. Reconstruction of bone ingrowth and segmentation of micro CT images of acellular 3D implants in sheep distal femur defect. First and second row: 2D slices of the 3D implant. Bone is labelled in yellow and metal in blue. Third and fourth row: bone ingrowth and close up high resolution detail of nascent bone. Pixel size 0.5 μm, panels' scale bars are 40 μm. Adapted with permission from Ref. [39] CC BY license. Scaffold-free. i) Scaffold-free tubular cardiac constructs on a needle array. Representative images of tubular constructs just after printing (A,B) and after culture for 7 days (C, D). ii) Needle-free tubular constructs (A) cultured for 7 days (B) and further electrically stimulated and effects analysed (C). Adapted with permission from Ref. [46]. Cell-laden. Representative images of the whole constructs prepared with hdECM (a) and adECM (b) at progressing days of cell culture. Confocal image of the whole construct prepared with adECM at day 14 of culture (c) showing live cells (green) and dead cells (red) (scale bar, 2 mm). An image of the whole construct reconstructed from B32 images taken at different positions. Representative images of apoptosis through TUNEL (d) and Live/Dead (e) assays. TUNEL assay displays minimal apoptotic cells, indicating the generated stress at 2 s−1 shear rate at the nozzle wall did not produce a deleterious effect on the encapsulated cells with comparable apoptosis to the non-printed gel (0 s−1). Cell viability was >95% at day 1 and > 90% at both day 7 and 14. Scale bars: (a–c) 2 mm, (d,e) 100 mm. Adapted from Ref. [50] with permission from publisher.