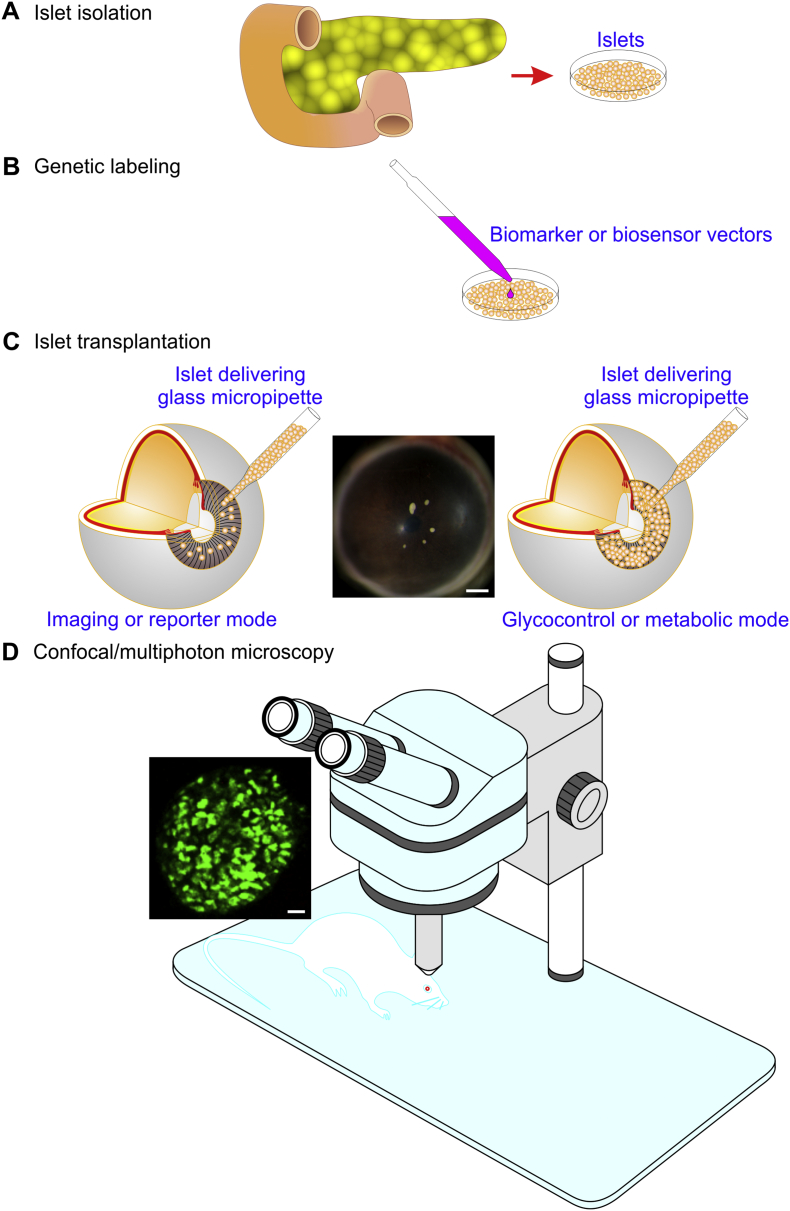
Fig. 2.
A scheme illustrating the practical procedures of the ACE technology. Typically, they include the folowing four steps. (A) Isolation of islets from the pancreas. (B) Genetic labeling of islets with biomarkers or biosensors. (C) Transplantation of islets into the ACE either in the imaging or reporter mode (left panel) or in the glycocontrol or metabolic mode (right panel). A stereomicroscopic photograph showing 5 B6 mouse islets implanted into the B6 mouse ACE (middle pannel). Calbriation bar = 500 μm. (D) Confocal/multiphoton microscopy of islets. A sample confocal image (left insert) showing a MIP-GFP islet engrafted on the MIP-GFP mouse ACE. Calibration bar = 20 μm. The ACE technology consists of two parts, namely the non-invasive technique for transplanting islets into the ACE including the first three steps and the ACE-based imaging technique of intraocular islets constituted by the last step.