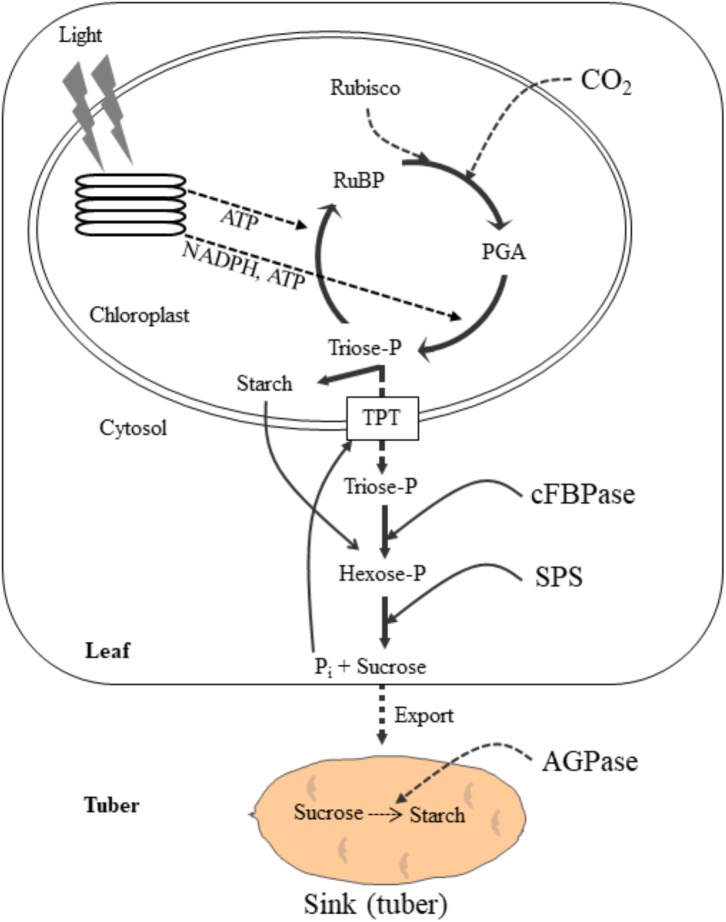
FIGURE 1.
A schematic diagram illustrating the photosynthetic carbon assimilation and its export to the potato tuber sink. In the chloroplast, light harvesting complexes absorb sunlight and generate ATP and NADPH through photosynthetic electron transport chain. The ATP and NADPH are then consumed by Calvin cycle to assimilate carbon to simple carbohydrate, triose phosphates (triose-P). Triose-P is either used to synthesize starch in the chloroplast or exported to cytosol in exchange for Pi through triose-P/Pi translocator. In the cytosol, the triose-P is then converted to sucrose via hexose phosphates using key sucrose biosynthetic enzymes, cFBpase and SPS. Sucrose is then transported to the sink (tuber), where it is converted to starch by AGPase. The synthesis of sucrose in the cytosol generates Pi which is exported to the chloroplast in the exchange for triose-P. Any stress that inhibit sucrose synthesis and its transport to sink (tuber) results in the feedback inhibition of photosynthesis due to Pi regeneration limitation. The broken arrows indicate the stress sensitive processes. RuBisCO, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase; RuBP, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate; TPT, triose phosphate translocator; cFBPase, cytosolic fructose bisphosphatase; SPS, sucrose phosphate synthase, AGPase: ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase. Modified from Hüner et al. (2016).