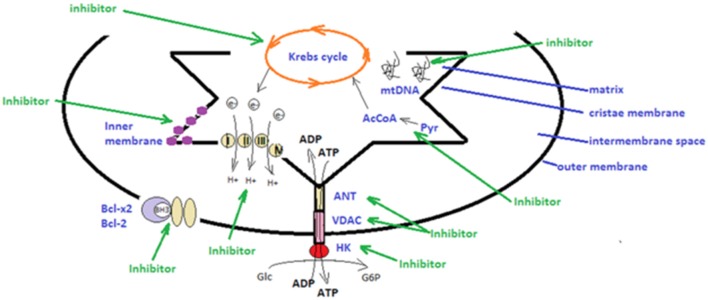
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of strategies utilized in mitochondrial therapeutic targeting. There are several types of mitocans that can target components appending to the outer mitochondrial membrane, to the inter-membrane space, to the cristae membrane and to the matrix. Hexokinase (HK), voltage-dependent anionic channel (VDAC) and adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) can be targeted by inhibitors that will disrupt main metabolic pathways and the anti-oxidative potential of tumor cells (48, 106, 129); The mitochondrial electron transport chain, producing energy by transporting electrons can be targeted by specific inhibitors (131, 132); BH3 mimetics can impair the function of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-x2 family proteins (76, 127); lipophilic cations can directly target the mitochondrial inner membrane and hinder mitochondrial transmembrane potential; compounds that affect directly the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle), affect the electrons stream into the electron transport chain (133); inhibitors that target the conversion of pyruvate (Pyr) to acetyl-CoA (AcCoA) hinder the tricarboxylic acid cycle (67); inhibitors that interfere with the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) affecting DNA polymerases or transcript levels (46, 83) (green arrows).