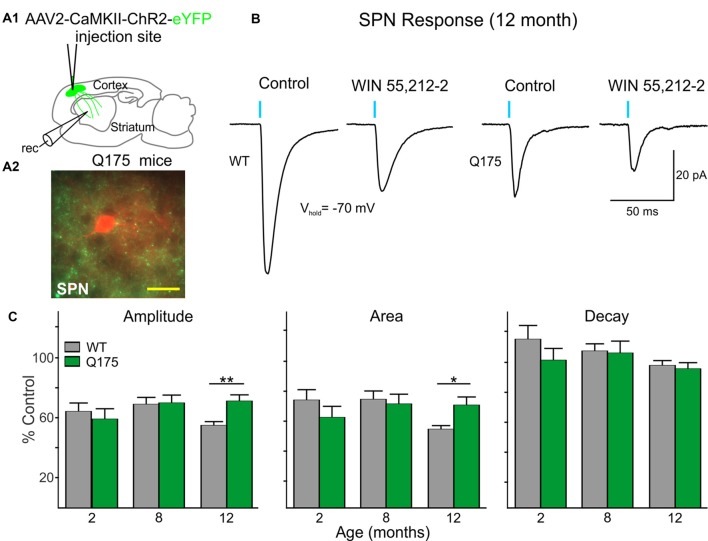
Figure 7.
Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) from the cortex are reduced in Q175 SPNs recorded in fully symptomatic mice and are less sensitive to modulation by WIN 55,212-2 compared to WT SPNs. (A1) Schematic of AAV injection site and recording area in Q175 mice for experiments examining CB1 receptor-mediated modulation of excitatory cortical inputs onto SPNs. (A2) Confocal z-stack image of a biocytin-filled SPN (red) that was recorded from an 8 months-old Q175 mouse. Corticostriatal processes expressing ChR2-eYFP are seen surrounding the recorded cell. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) Sample traces of optically-evoked, cortical-induced glutamatergic responses in WT and Q175 SPNs before (Control) and at the end of 20 min incubation with WIN 55,212-2 (3 μM). (C) Summary of the effects of WIN 55,212-2 (3 μM) on optically-evoked EPSCs from WT and Q175 SPNs from 2-, 8- and 12-month-old mice. Average response properties (amplitude, area and decay time) are reported as a percentage of the Control response. Significant differences were determined using two-way ANOVAs and appropriate post hoc analyses, where *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.