Figure 1.
Lymphovascular Macrophages in TNBC Mouse Models Are Retained through Binding of β4 Integrin to Laminin-5
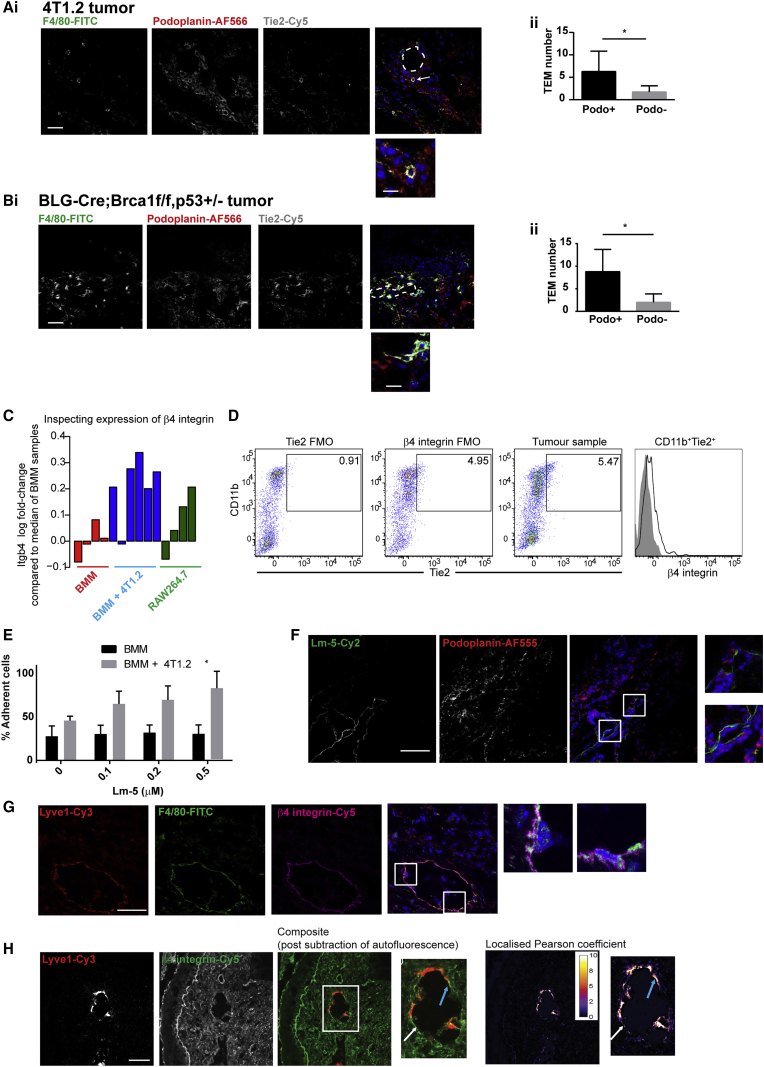
(A and B) Tumor sections from 4T1.2 (A) and BLG-Cre;Brca1f/f,p53+/− (B) were stained with F4/80-FITC, podoplanin-AF555, and Tie2 -Cy5-conjugated antibody. F4/80+Tie2+ macrophages within podoplanin+ areas versus those in other areas were quantified per field of view (FOV). Vessel lumen is outlined; arrow indicates a macrophage within a podoplanin+ area. Images were acquired with a ×40 air objective. Scale bars, 100 μm (main image) and 25 μm (zoomed inset).
(C) Array-derived expression profile of β4-integrin (Itgb4) across samples. Barplot shows log2 fold change of normalized expression value for β4 integrin (ratio of the median value of probe in BMM samples).
(D) Day-12 4T1.2 tumors were disaggregated. Tie2 and β4 integrin FMO controls are indicated in 2 left panels. Right dot plot and histogram depict β4-integrin-expressing macrophages from representative 4T1.2 tumor (n = 8).
(E) BMMs co-cultured alone or with 4T1.2-GFP cells plated on laminin-5. The percentage of adherent cells were quantified in triplicate (n = 2).
(F and G) 4T1.2 tumor sections were stained with laminin-5-Dylight488 and podoplanin-AF555 (F), and Lyve1-Cy3, F4/80-FITC, and β4 integrin-Cy5 (G); inset shows F4/80+β4 integrin+ macrophages around lymphatic endothelium.
(H) Stained sections (Lyve1-Cy3 and β4 integrin-Cy5) were imaged using a custom-built microscope (×20 air objective). Area of distinct β4 integrin and Lyve1 within lymphatic vessel (white arrow) and area of close contact between β4 integrin and Lyve1 (blue arrow) are indicated. Scale bars, 50 μm (main panels) and 25 μm (inset).