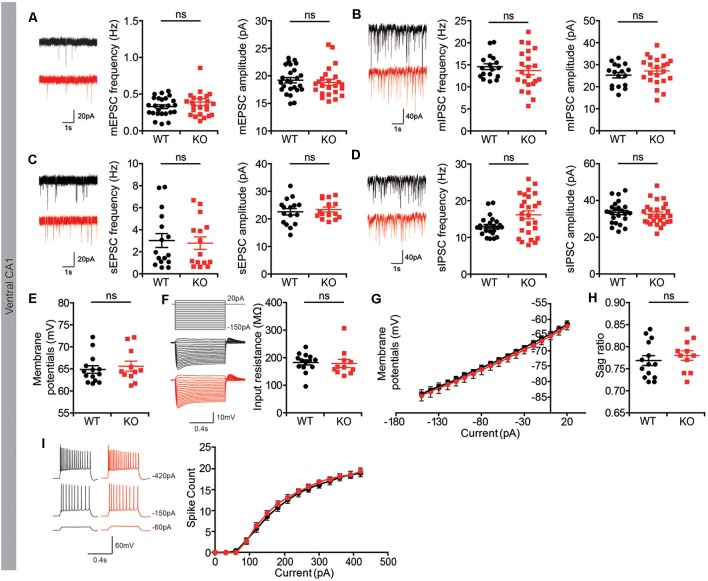
Figure 3.
Normal spontaneous synaptic transmission in Lrrc4c−/− hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. (A) Normal frequency and amplitude of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) in ventral CA1 pyramidal neurons of Lrrc4c−/− mice (2–4 months; male). n = 25 neurons from four mice (WT), n = 24 (4; KO), ns, not significant, Mann-Whitney test. (mEPSC frequency: U = 279.5; p = 0.8740; mEPSC amplitude: U = 261.0; p = 0.4447). (B) Normal frequency and amplitude of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) in ventral CA1 pyramidal neurons of Lrrc4c−/− mice (2–4 months; male). n = 17 (4; WT), n = 22 (4; KO), ns, not significant, Student’s t-test. (mIPSC frequency: t(37) = 0.7133; p = 0.4801; mIPSC amplitude: t(37) = 1.028; p = 0.3107). (C) Normal frequency and amplitude of spontaneous EPSC (sEPSC) in ventral CA1 pyramidal neurons of Lrrc4c−/− mice (2–4 months; male). n = 16 (3; WT), n = 15 (3; KO), ns, not significant, Student’s t-test. (sEPSC frequency: t(29) = 0.28; p = 0.7815; sEPSC amplitude: t(29) = 0.5433; p = 0.5911). (D) Normal frequency and amplitude of spontaneous IPSCs (sIPSCs) in ventral CA1 pyramidal neurons of Lrrc4c−/− mice (2–4 months; male). n = 31 (5; WT), n = 26 (5; KO), ns, not significant, Mann-Whitney test (frequency) and Student’s t-test (amplitude). (sIPSC frequency: U = 218; p = 0.0692; sIPSC amplitude: t(49) = 0.5373; p = 0.5935). (E–I) Normal resting membrane potential (E), input resistance (F,G), sag ratio (H), current firing curves (I) in ventral CA1 pyramidal neurons of Lrrc4c−/− mice (2–4 months; male). n = 14 (3; WT), n = 11 (3; KO), ns, not significant, Mann-Whitney test, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test (E: U = 71; p = 0.7675; F: U = 55; p = 0.2441; H: U = 61; p = 0.3937).