S3.
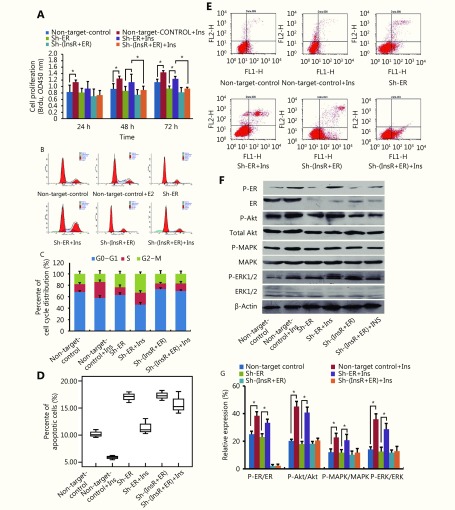
Insulin promotes ECC-1 cell progression via the estrogen receptor (ER) by activating the PI3K and MAPK pathways. (A) BrdU enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of the effects of insulin stimulation on ECC-1 cell proliferation after knockdown of ER and/or insulin receptor (InsR). (B, C) Flow cytometry analysis of the effects of insulin stimulation on ECC-1 cell cycle distribution after knockdown of ER and/or InsR. (D, E) The percentage of apoptotic ECC-1 cells (after knockdown of ER and/or InsR) treated with insulin was determined by flow cytometry analysis using Annexin V-FITC antibodies. (F, G) Western blot analysis of the effects of insulin treatment on the ratios of phosphorylated (p)-ER/ER, p-Akt/Akt, p-MAPK/MAPK, and p-ERK/ERK in ECC-1 cells after knockdown of ER and/or InsR. *P < 0.05 for all experiments.