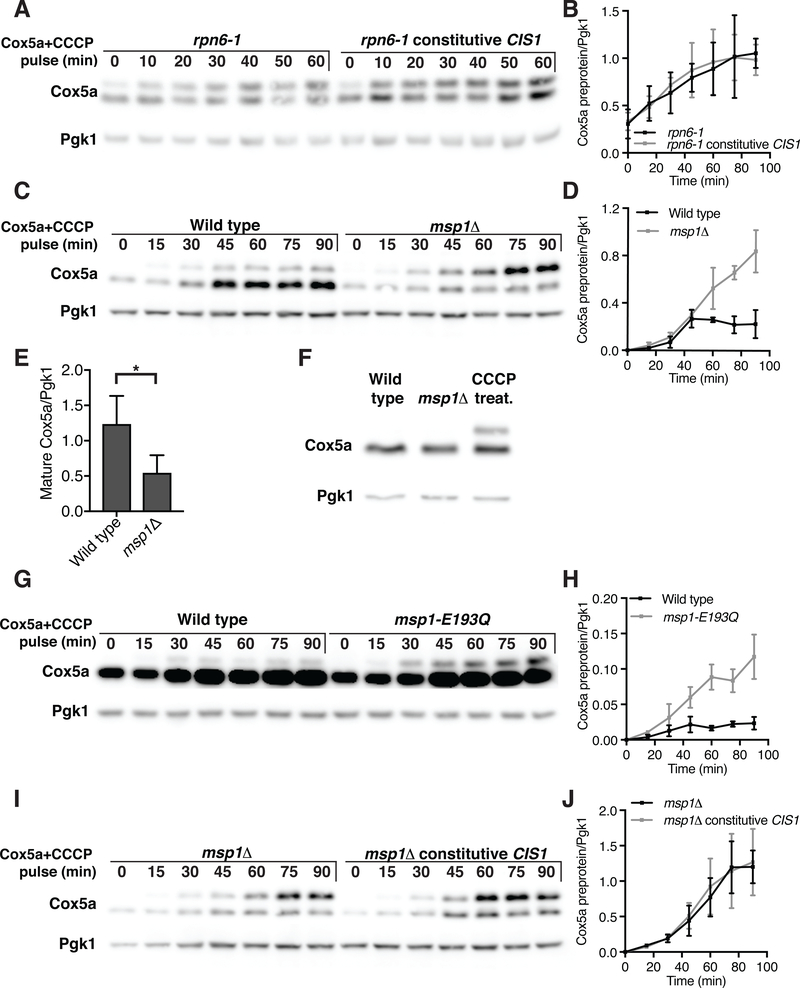
Fig. 6. Cis1 and Msp1 are required for preprotein clearance following mitochondrial import stress.
(A) rpn6–1 or rpn6–1 TEF2-CIS1 cells were grown at room temperature in the presence of methionine. Cells were then transferred into medium lacking methionine with 20μM CCCP at 30°C. The accumulation of Cox5a-V5 preprotein (encoded by MET25-COX5a) is shown. (B) Quantification of (A); Cox5a preprotein levels from 4 independent experiments. Data are mean +/− SD. (C) Wild type or msp1Δ cells were grown at 30°C with methionine and treated as in (A). (D) Quantification of (C); Cox5a preprotein levels from 4 independent experiments. Data are mean +/− SD. (E) Quantification of (C); Mature Cox5a levels 60 min following induction. n=4. Data are mean +/− SD. Statistics were performed using the Student’s t-test. *p ≤ 0.05. (F) Immuno-blot analysis of Cox5a-V5 from wild-type cells, wild-type cells treated with 20μM CCCP for 1h, or msp1Δ cells. (G) Wild type cells or cells expressing msp1-E193Q from the inducible GAL1–10 promoter were grown in the presence of galactose for 6h. Cells were then transferred to medium lacking methionine and containing 20μM CCCP and the accumulation of inducible Cox5a-V5 preprotein (encoded by MET25-COX5a) was examined. Note that Cox5a levels were higher in this experiment because MET25-COX5a expression is higher in medium containing raffinose/galactose than glucose (Fig. S5B). (H) Quantification of (G); Cox5a preprotein levels from 3 independent experiments. Data are mean +/− SD. (I) msp1Δ cells or msp1Δ cells expressing TEF2-CIS1 were treated as in (C). Note that the experiment shown in (C) was performed in parallel and results can thus be directly compared. (J) Quantification of (I); Cox5a preprotein levels from 3 independent experiments. Data are mean +/− SD.