Fig. 2.
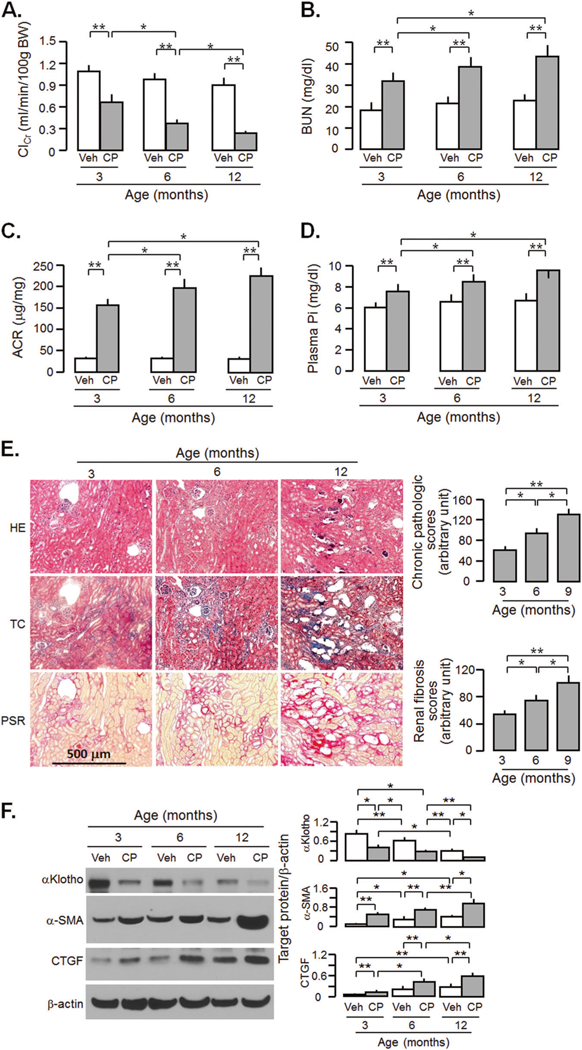
Aged mice are more vulnerable to acute cisplatin (CP) nephrotoxicity and at higher risk for CKD. WT mice at 3, 6, and 12 months old were injected with CP (10mg/Kg) or normal saline as vehicle (veh) and sacrificed at 20 weeks. a Creatinine clearance (ClCr). b Blood urea nitrogen (BUN). c Plasma phosphate (Pi). d Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR). e Kidney histology assessed by HE, TC, and PSR stain (scale bar = 500 μm); and semi-quantitative assessment (right panel including chronic pathologic score based on HE stain and renal fibrosis score based on PSR stain). f αKlotho and fibrotic markers in the kidney. Left panel: representative immunoblot for αKlotho, α-SMA, and CTGF in total kidney lysates. Right panel: summary of all immunoblots. Data are expressed as means ± SD from each group and statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test, and significance was accepted when *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 between two groups. HE Hematoxylin and Eosin stain; TC Trichrome stain; PSR Picrosirius red stain
