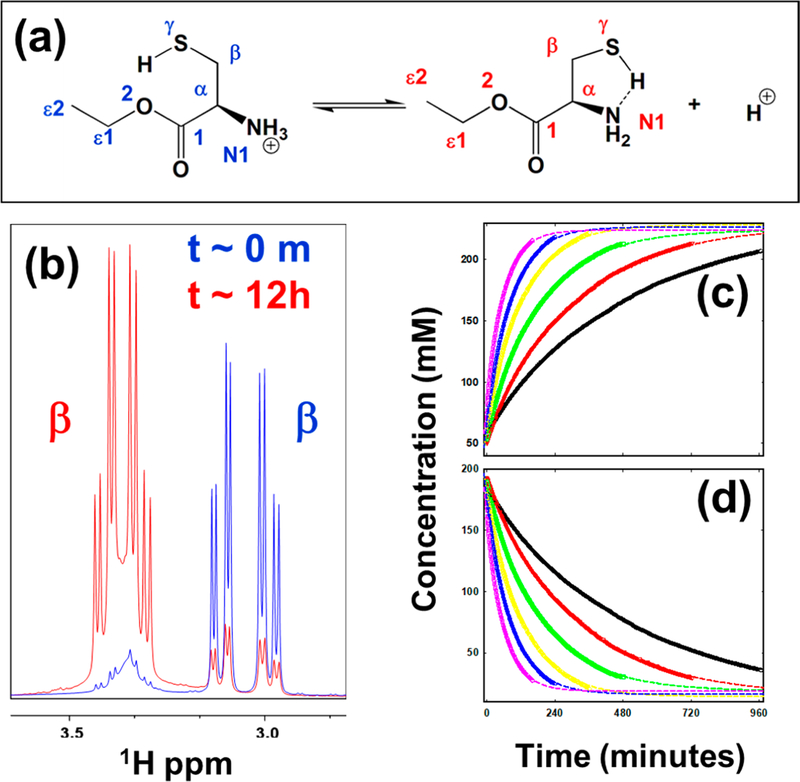
Figure 1.
Determination of molecular thermodynamic parameters from the rate of oxidation. (a) Structural change due to the oxidation of the thiol proton in the model system L-cysteine ethyl ester ([CysEE-H] +). (b) Chemical shift changes due to the oxidation-mediated changes in L-cysteine ethyl ester in the sub-spectral region corresponding to the β -protons of the reactant (blue) and that of the product (red) obtained in dissolving the DMSO-d6. The first-order kinetics of the reaction process of L-CysEE at various temperatures are also shown. (c) The reduction of the reactant ([CysEE-H] +) measured directly by NMR for various sample temperatures, and the corresponding increase of the ionized product ([CysEE]) (d). The experimental measurements are shown as symbols, and the non-linear least square fit to the respective experimental data are shown as dashed lines (samples temperatures are given in the legends). Figure reproduced with permission [24].