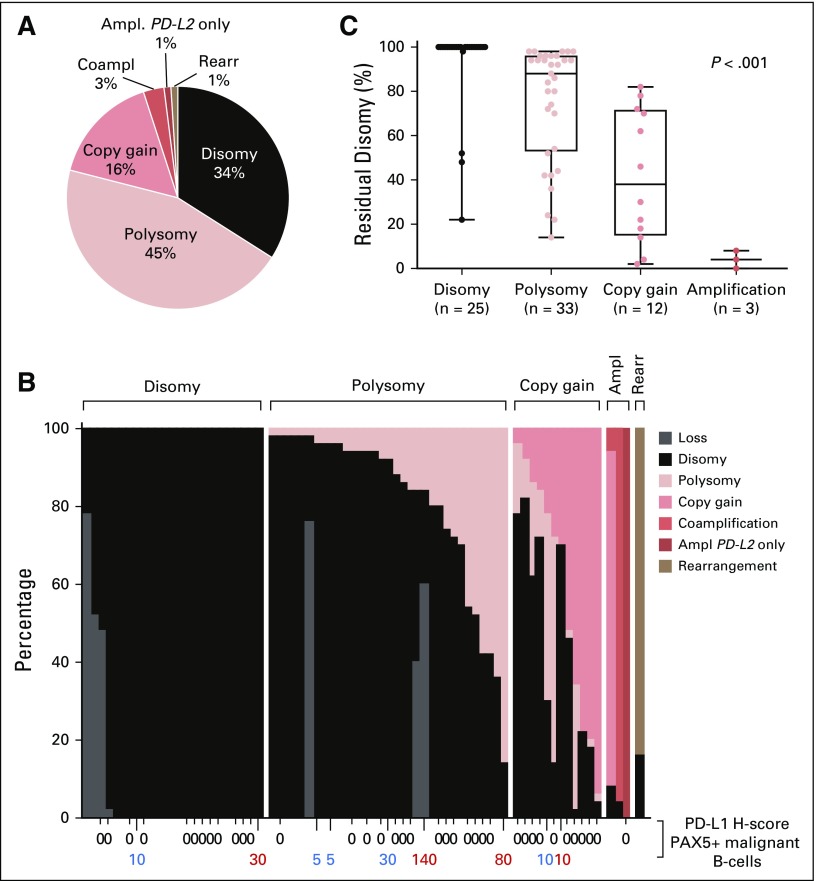
FIG 3.
Prevalence and spectrum of 9p24.1 genetic alterations and association of residual disomy with 9p24.1 genetic categories. (A) Prevalence of 9p24.1 genetic alterations in evaluated diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs). (B) Spectrum of 9p24.1 alterations in evaluated DLBCLs. Each patient is classified by the highest observed level of 9p24.1 alteration in tumor cells: polysomy, copy gain, amplification (Ampl), or rearrangement (Rearr). Individual patients are visualized as columns on the x-axis. Percentages of tumor cells with monosomy/relative copy loss (gray), disomy (black), polysomy (light red), copy gain (medium red), amplification (dark red), and rearrangement (brown) are depicted on the y-axis. In cases with evaluable 9p24.1 status and PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (n = 46), programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression (H-score) on PAX5-positive malignant B cells is indicated below the x-axis (membranous PD-L1 in red, cytoplasmic PD-L1 in blue). (C) Percentage of tumor cells with residual 9p24.1 disomy in DLBCLs classified by 9p24.1 genetic categories (P < .001 from ordinary one-way analysis of variance of unpaired t test data). Coampl, coamplification; PD-L2, programmed death ligand 2.