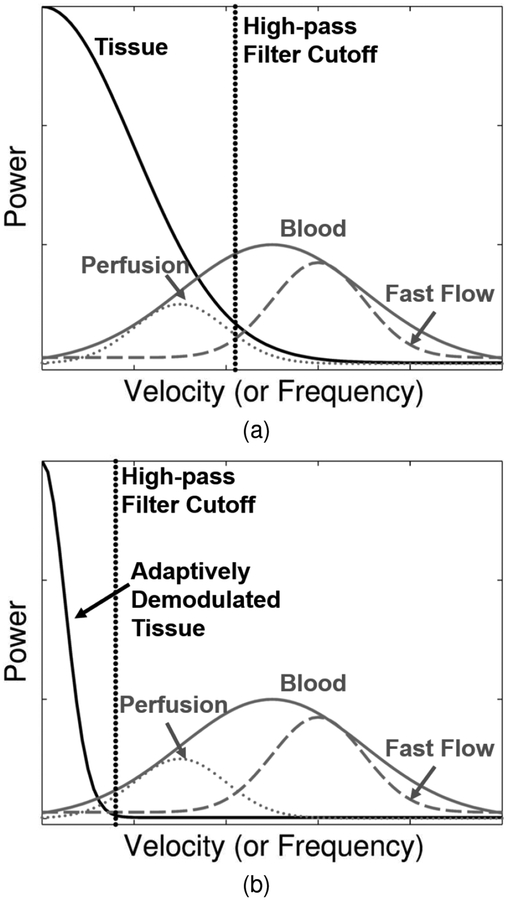
Fig. 1.
(a) Patient and sonographer motion causes spectral broadening of tissue clutter signal (black) causing it to overlap with low velocity blood flow or perfusion signal (dotted gray). Conventional high-pass tissue clutter filters (dotted black) preserve only high velocity blood signal (dashed gray). The full blood distribution is depicted as the solid gray curve. (b) Adaptive demodulation suppresses the tissue clutter bandwidth, allowing for perfusion signal to pass through the tissue clutter filter.