Figure 2.
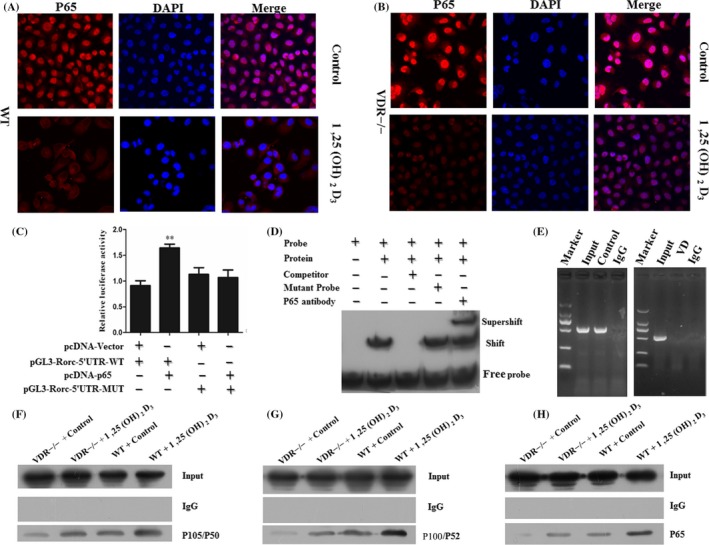
Rorc was a downstream gene of the transcription factor P65. (A, B) WT and VDR−/− Th17 cells were fixed and stained for DAPI (nucleus) and p65. Robust NF‐κB is represented by high fluorescence levels of the p65 transcription factor in the nucleus of VDR−/− Th17 cells with 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment. (C) Plasmid pcDNA‐Vector, pGL3‐Rorc‐5′UTR‐WT, pcDNA‐p65 and pGL3‐Rorc‐5′UTR‐MUT reporter were co‐transfected and the luciferase was measured. (D) EMSA‐Super‐shelf assay was performed to identify the P65‐binding sites in the Rorc promoter. Nuclear protein extracts are prepared from Th17 cells and were incubated with a biotin‐labelled DNA probe, followed by chemiluminescent EMSA. The unlabelled probe served as a cold competitor, and its mutant served as a negative control. The specificity of the P65‐binding motif was confirmed by the ability of P65‐specific antibody to block the DNA complex shift. An arrow indicates the P65 DNA‐binding complex. (E) ChIP DNA agarose gel results of DNA sequences immunoprecipitated by normal rabbit IgG or a rabbit anti‐P65 antibody amplified by Rorc promoter‐specific primers. Control represents the vehicle and VD represents the 1,25(OH)2D3. (F) Co‐IP experiments were carried out in WT and VDR−/− Th17 cells with or without 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment. Western blot analysis of whole cell lysate and co‐IP samples of IgG or anti‐P105/P50 antibody. (G) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysate and co‐IP samples of IgG or anti‐P100/P52. (H) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysate and co‐IP samples of IgG or anti‐P105/P50 antibody. Data represent 3 independent experiments (average and s.e.m of triplicate samples). **P < .01
