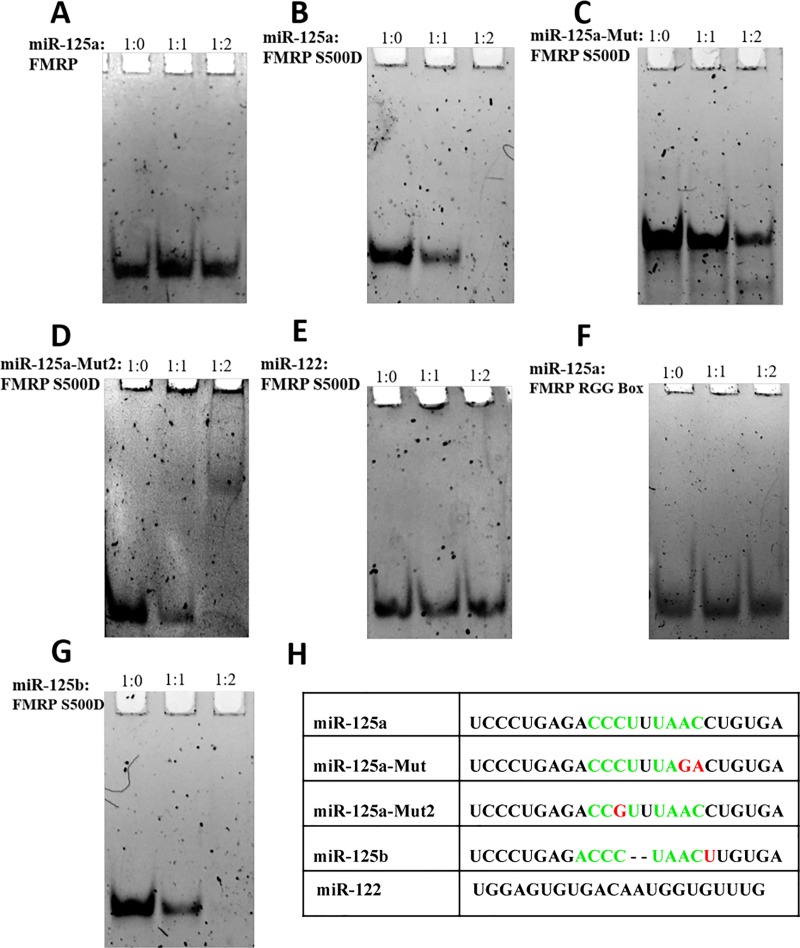
Fig 5. EMSA binding of FMRP ISO1, FMRP S500D binding to miR-125a.
EMSA (15% non-denaturing gel) of miR-125a with FMRP ISO1 (A) and FMRP S500D (B). Free 200 nM miR-125a (lane 1) was incubated with a 1:1 (lane 2) and 1:2 (lane 3) RNA: protein ratio. (C) and (D). EMSA (15% non-denaturing gel) of two miR-125a mutants, miR-125a-Mut and miR-125a-Mut2, with FMRP S500D. Free 200 nM mutant miR-125a (lane 1) was incubated with a 1:1 (lane 2) and 1:2 (lane 3) RNA: FMRP S500D. (E). EMSA (15% non-denaturing gel) of an unrelated miRNA, miR-122, with FMRP S500D. Free 200 nM miR-122 (lane 1) was incubated with a 1:1 (lane 2) and 1:2 (lane 3) RNA: FMRP S500D. (F). EMSA (15% non-denaturing gel) of miR-125a with the FMRP RGG box. Free 200 nM miR-125a (lane 1) was incubated with a 1:1 (lane 2) and 1:2 (lane 3) RNA: FMRP RGG peptide ratio. (G) EMSA (15% non-denaturing gel) of miR-125b with FMRP S500D. Free 200 nM miR-125b (lane 1) was incubated with a 1:1 (lane 2) and 1:2 (lane 3) RNA: FMRP S500D ratio. The gels were visualized by staining with SYBR Gold for 15 minutes. The miRNA sequences used are shown in (H) with the predicted binding sites for the KH domains highlighted in green; miR-125a-Mut, miR-125a-Mut2, miR-125b, and miR-122 sequences are also shown for comparison with the differences from miR-125a highlighted in red.