Figure 1.
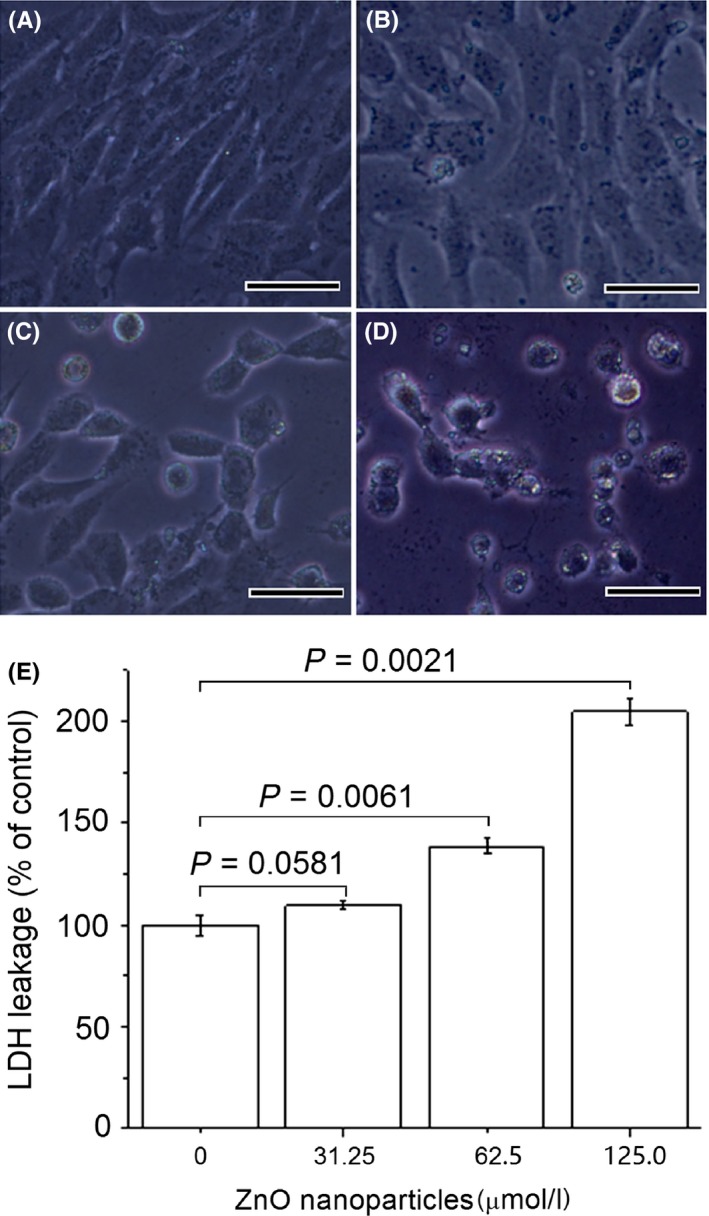
Effects of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on cell morphology and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from DMEM supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum‐grown 661W cells. Cells were exposed to different concentrations of ZnO nanoparticles (ie, 0, 31.25, 62.5, 125.0 μmol/L) for 24 h before assessing morphology and LDH release. Negative control was 661W cells not exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. (A) untreated cells; (B) cells treated with 31.25 μmol/L of ZnO NPs; (C) cells treated with 62.5 μmol/L of ZnO NPs; (D) cells treated with 125.0 μmol/L of ZnO NPs; and (E) the results of histogram analysis for LDH release. P<.05 is considered significant compared with negative control, NPs=nanoparticles and bar=20 μm
