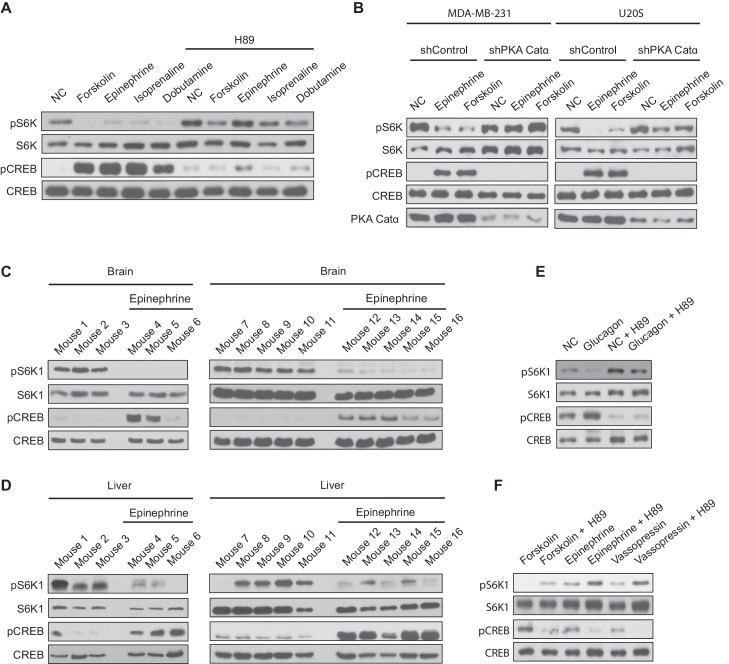
Figure 7. Activation of Gαs-coupled GPCRs inhibit mTORC1 activity in vivo.
(A) MDA-MB-231 cells were pretreated with or without the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor H89, and then treated with or without 10 μM forskolin, 10 μM epinephrine, 10 μM isoprenaline, or 10 μM dobutamine for 1 h. mTORC1 activity was analyzed by protein immunoblotting for the phosphorylation status of S6K1 (pS6K1) at Thr 389. Phosphorylation of CREB (pCREB) at Ser 133 was used as a positive control for the increase of cAMP after Gαs-coupled GPCR stimulation. Both S6K1 and CREB were used as lysate loading controls. NC denotes normal conditions. (B) MDA-MB-231 and U20S stable cell lines expressing control shRNA (shControl) or shRNA targeting the PKA catalytic α subunit (shPKA Cat α) were treated with or without 10 μM forskolin or 10 μM epinephrine. mTORC1 activity and loading controls were analyzed as described in (A). PKA Catα was also immunoblotted as a control to show the level of PKA Catα. NC denotes normal conditions. (C) Mice were injected with either epinephrine (0.75 ug/g) or propranolol (0.04 mg/g), and 30 min later brain tissues were processed and analyzed for mTORC1 activity by immunoblotting for the phosphorylation status of S6K1 (pS6K1) at Thr 389. Phosphorylation of CREB (pCREB) at Ser 133 was used as a positive control for the increase of cAMP after Gαs-coupled GPCR stimulation (β2 adrenergic receptor). Both S6K1 and CREB were used as lysate loading controls. (D) Mice were injected with either epinephrine (0.75 ug/g) or propranolol (0.04 mg/g), and 30 min later livers were processed and mTORC1 activity, cAMP levels (stimulation of β2 adrenergic receptor), and loading controls were analyzed as described in (A). (E) Primary mouse hepatocytes were treated with 2 μM glucagon for 1 h, and mTORC1 activity, cAMP levels, and loading controls were analyzed as described in (A). (F) Primary mouse hepatocytes were pretreated with or without PKA inhibitor H89, and then treated with 10 μM forskolin, 10 μM epinephrine, or 10 μM vasopressin for 1 h, and mTORC1 activity, cAMP levels, and loading controls were analyzed as described in (A).