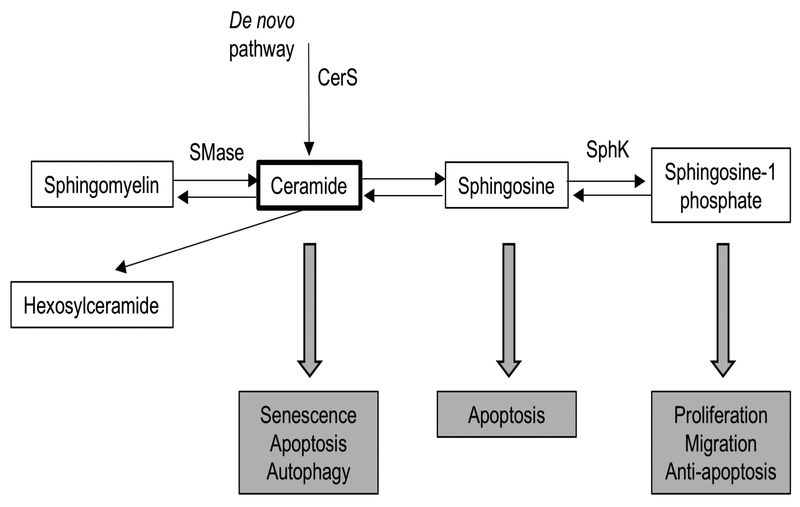
Figure 1:
Overview of sphingolipid metabolism and biological roles of bioactive sphingolipid species. Figure adapted from Hannun & Obeid (2008)22. Only enzymes thought to be potential therapeutic targets shown in this figure. Ceramide is synthesized through a de novo pathway catalyzed by serine palmitoyltransferase and ceramide synthase (CerS) or through the breakdown of sphingomyelin by sphingomyelinases (SMase). Sphingosine can be generated from ceramide by ceramidases and further converted into sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) by sphingosine kinase (SphK). Ceramide and sphingosine are overall pro-apoptotic lipids, whereas S1P has overall anti-apoptotic effects. Sphingomyelin and hexosylceramide are not known to be bioactive sphingolipids.