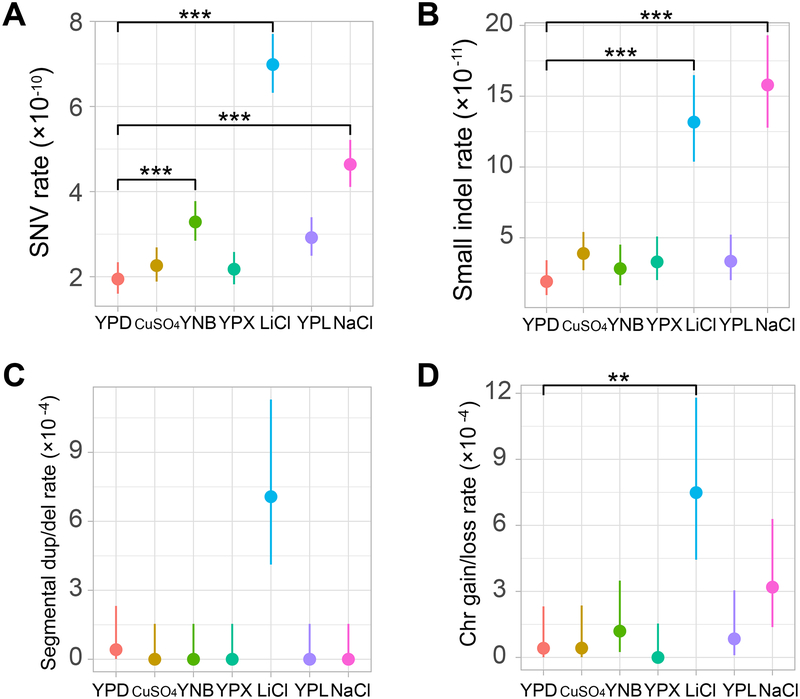
Figure 2. Rates of (A) SNV, (B) small indel, (C) segmental duplication/deletion, and (D) whole-chromosome gain/loss mutations differ in the seven environments.
The SNV rate is measured by the number of mutations per nucleotide per cell division, the small indel rate is measured by the number of mutations per nucleotide per cell division, the segmental duplication/deletion rate is measured by the number of mutations per cell division, and the whole-chromosome gain/loss rate is measured by the number of mutations per cell division. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals predicted from the Poisson distribution of the number of mutations. Mutation rate variation among the seven environments is significant in each panel (P < 10−4, ANOVA). Difference in mutation rate between a medium and YPD is assessed by a Wilcoxon rank-sum test followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple testing (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). In all panels, the six non-YPD environments are ordered from high to low growth rates on the X-axis. See also Figure S1, Tables S2–S3, and Data S1.