Figure 1.
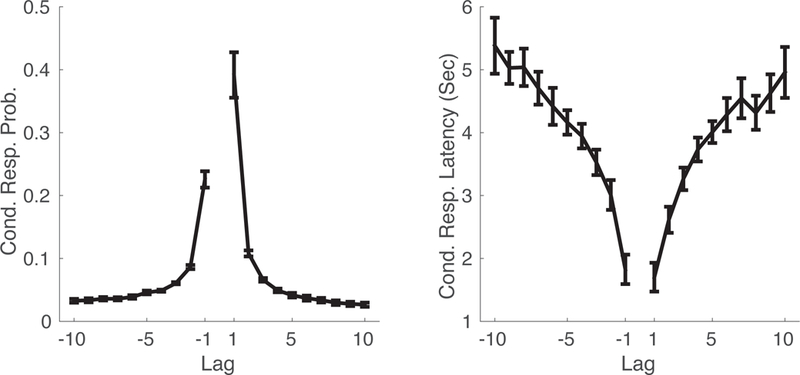
The contiguity effect: Recall of one event triggers recall of other events that occurred near in time. (A) The conditional-response probability as a function of lag (lag-CRP) shows the probability of recalling an item from serial position i + lag immediately following recall of an item from serial position i. (B) The conditional response latency as a function of lag (lag-CRL) shows the mean inter-response time between successive recalls of items from serial positions i and i + lag. Data are from Experiment 4 of the Penn Electrophysiology of Encoding and Retrieval Study (PEERS). Subjects studied lists of 24 words for delayed free recall. Error bars are 95% within-subject confidence intervals (Loftus & Masson, 1994).
