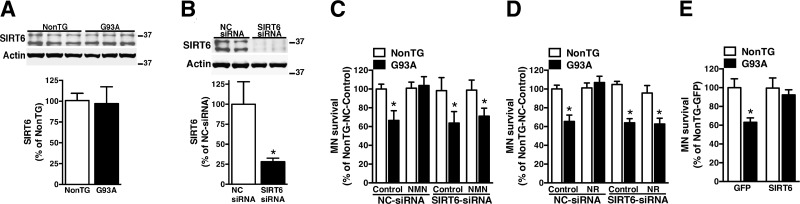
Figure 5.
SIRT6 is necessary for the protection conferred by NAD+ precursors in astrocyte motor neuron cocultures. A) SIRT6 protein levels in confluent nontransgenic (NonTG) or hSOD1G93A (G93A) spinal cord astrocyte cultures. Actin levels were used as loading control. Each lane represents an independent biological replicate. For quantification (lower panel), both SIRT6 isoforms were measured. B) Confluent astrocyte cultures were transfected with an NC-siRNA or SIRT6-siRNA and, 48 h later, SIRT6 protein levels were analyzed by Western blot. The lower panel shows the quantification of SIRT6 expression after correction by actin levels. C) Confluent NonTG or G93A spinal cord astrocyte cultures were transfected with NC-siRNA or SIRT6-siRNA and, 48 h later, treated with vehicle (control) or 5 mM NMN. Twenty-four hours after NMN treatment, astrocyte cultures were washed, and purified motor neurons from E12.5 mice were plated on top of the astrocyte monolayer. Motor neuron survival was assessed 72 h later. *P < 0.05, significantly different from NonTG-NC control astrocytes. D) The same experimental set up as in C, except that astrocytes were treated with 5 mM NR. *P < 0.05, significantly different from NonTG-NC control astrocytes. E) Confluent NonTG and G93A spinal cord astrocyte cultures were transfected with adenovirus-expressing GFP or SIRT6 and, 48 h later, purified motor neurons from E12.5 mice were plated on top of the astrocyte monolayer. *P < 0.05, significantly different from NonTG-GFP astrocytes. For C–E, each data bar represents the mean ± sd of at least 3 independent coculture experiments.