Figure 3.
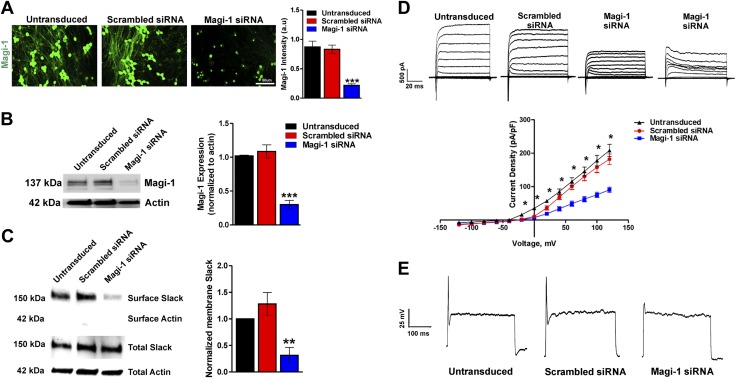
Magi-1 knockdown decreases ionic currents and excitability in DRG neurons. A) Representative Magi-1 immunolabeling from cultured DRG neurons 3 d after transfection with Magi-1–targeting siRNA and nontargeting scrambled siRNA (left) using a previously validated polyclonal Magi-1 antibody. Quantification of Magi-1 immunoreactivity is shown on the right. The integrated fluorescence intensity was calculated as the product of the area and the mean pixel intensity using Metamorph software. Values from 4 independent DRG neuronal cultures per experimental condition were analyzed. Values are expressed as means ± sem [ANOVA, F(2,11) = 32.25]. Scale bar, 50 μm. ***P < 0.001 vs. respective controls. B) Representative immunoblots depicting Magi-1 expression after siRNA-mediated Magi-1 knockdown. Magi-1 antibodies normally detect multiple splice variants as indicated by the multiple bands observed on Western blot. Quantification of Magi-1 knockdown in DRG neurons (right). Three different cultures per experimental condition were analyzed. Values expressed as means ± sem [ANOVA, F(2,6) = 42.94]. ***P < 0.001 vs. respective controls. C) Representative immunoblots of surface biotinylation from DRG neurons after Magi-1 knockdown (left). Quantification of Slack channel surface expression is shown on the right. Three independent cultures were analyzed, and values are expressed as means ± sem [ANOVA, F(2,6) = 10.84]. **P < 0.01 vs. respective controls. D) Representative current traces of IK in DRG neurons after Magi-1 knockdown (top). A total of 11–12 neurons per experimental condition were analyzed, and values are expressed as means ± sem. *P ≤ 0.05. E) Representative Action Potential (AP) firing from neurons after siRNA-mediated Magi-1 knockdown during suprathreshold current stimulation (400 pA) for 1000 ms, untransduced (10 out of 10), scrambled DRG neurons 12 out of 12 fire 1 AP, whereas 12 out of 18 neurons transfected with Magi-1 siRNA failed to fire a single AP. A.u., arbitrary unit.