Figure 4.
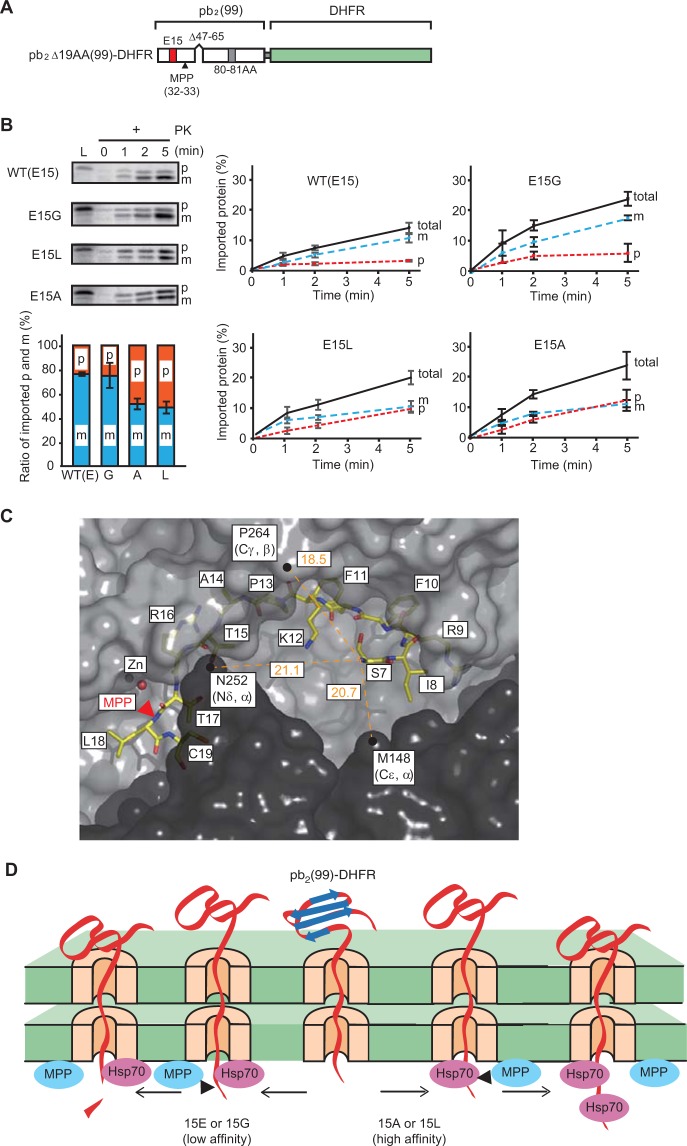
Competition between the motor-component binding to presequence and presequence cleavage by MPP. (A) Schematic representation of pb2Δ19AA(99)-DHFR and its derivatives used for import and MPP cleavage analyses. The first 99 residues of the cytochrome b2 precursor (the 80-residue presequence with the deletion of residues 47–65 in the intermembrane space sorting signal and with the 80N81E → 80A81A mutation at the second processing site, plus 19 residues of the mature protein) was attached to the N-terminus of DHFR. With these mutations, pb2Δ19AA(99)-DHFR fusion proteins are targeted to the matrix and do not receive the second processing of the presequence by Imp130,35. (B) In vitro import of the radiolabeled pb2Δ19AA(99)-DHFR fusion proteins into mitochondria. The fusion protein (WT) or its variants bearing a mutation E15G, E15A, or E15L were incubated with isolated mitochondria for various time at 25 °C, and proteinase K (PK)-protected fractions (upper left panels) were quantified and plotted against time (central and right panels). L, 5% (WT and E15L) or 10% (E15G and E15A) of the input as loading controls. The amounts of radiolabeled proteins added to each reaction are set to 100%. The amounts of the imported proteins with (m) and without (p) the MPP cleavage at 5 min import were plotted (lower left panel, the total amounts (m + p) are set to 100%). Values are means ± SD. Full-length gel images are presented in Supplementary Fig. S1. (C) The crystal structures of the cleavage-deficient mutant of yeast MPP in a complex with the cytochrome oxidase subunit IV presequence peptide (1HR8). Two subunits of the MPP homo-dimer are represented by their surface diagram (dark gray for subunit a and light gray for subunit b) and the peptide (residues 7–18) drawn in stick form. Residues 1–6 are not visible. MPP cleavage site of the peptide between residues 17 and 18 are shown by the red arrowhead. The distances (Å) between S7 (Nα) of the peptide and the MPP residues at the entrance of the dimer interface (Nδ of N252 of subunit b, Cγ of P264 of subunit b, and Cε of M148 in subunit a) are indicated in orange. The N-terminal residue of the peptide corresponds to position -17 (from the MPP cleavage site) and is supposed to be close to the entrance. This panel suggests that MPP would sterically compete with mtHsp70 in binding to residue 15 of the pb2 presequence. (D) Model of competition between presequence cleavage by MPP and binding by mtHsp70 in the matrix. In this figure, mtHsp70 was assumed to be a presequence-binding protein of the import motor system for simplicity.