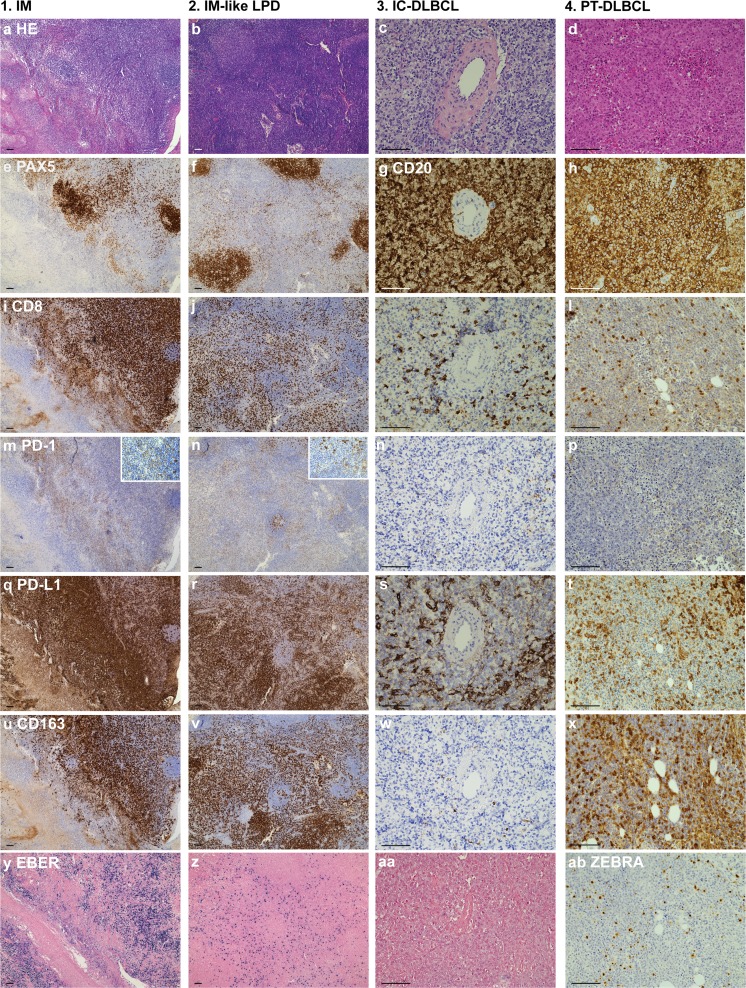
Fig. 2.
Representative cases. Representative cases of primary infectious mononucleosis in an immunocompetent young adult (column 1), infectious mononucleosis-like reactivation in a PT-patient (column 2), DLBCL in an immunocompetent patient (column 3) and PT-DLBCL highlighting the similarities between the different lesions. (a-d) hematoxylin and eosin stain; (e-f) Pax5 IHC stains and (g-h) CD20 IHC stains marking B cells; (i-l) CD8 IHC stains marking cytotoxic T cells; (m-o) PD-1 IHC stains and (q-t) PD-L1 IHC stains marking immune checkpoint therapy targets, the cutouts in (m-n) illustrate the difference in PD-1 staining intensity between cytotoxic T cells and follicular T-helper cells; (u-x) CD163 IHC stains marking macrophages; (y-aa) EBV RNA (EBER) in situ hybridization marking EBV presence; (ab) ZEBRA[BZLF] IHC stain for lytic viral replication. Abbreviations; IM: Infectious mononucleosis; LPD: lymphoproliferative disorder; IC: immune competent; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PT: post-transplant; scale bar = 100 μm; IHC, immunohistochemical