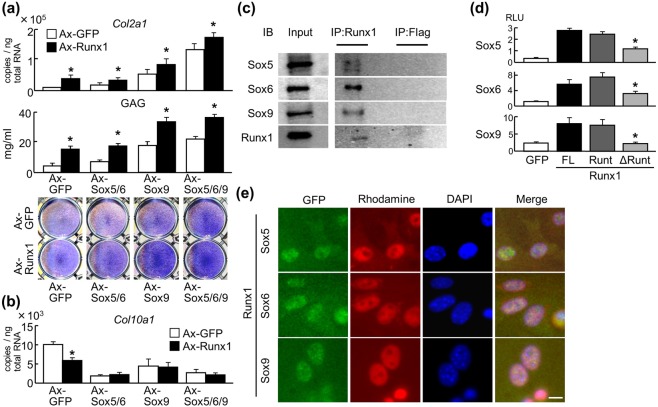
Figure 3.
Interaction between Runx1 and Sox proteins. (a) Levels of Col2a1 mRNA, glycosaminoglycan (GAG), and Toluidine blue staining in C3H10T1/2 cells adenovirally transduced with Runx1 in combination with GFP, Sox5 + Sox6, Sox9, or Sox5 + Sox6 + Sox9. Data are expressed as means (bars) ± SD (error bars) of six samples per group *P < 0.01 versus each Ax-GFP control. (b) Levels of Col10a1 mRNA in ATDC5 cells adenovirally transduced with Runx1 in combination with GFP, Sox5 + Sox6, Sox9, or Sox5 + Sox6 + Sox9. Cells were cultured in pellets for 3 days after adenoviral transduction. Data are expressed as means (bars) ± SD (error bars) of four samples per group *P < 0.01 versus each Ax-GFP control. (c) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay using cell lysates of human articular chondrocytes. Cell lysates underwent IP with an antibody to Flag or Runx1, and were then immunoblotted with the other antibody. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 2. (d) Mammalian two-hybrid assay by transfection of luciferase reporter vectors expressing GAL4–Runx1 (FL, full-length Runx1; Runt, the runt domain only; and ΔRunt, Runx1 mutant lacking the runt domain) and VP16–Sox proteins with GAL4 binding sites into HuH-7 cells. Data are expressed as means (bars) ± s.d. (error bars) of four samples per group *P < 0.01 vs. FL. (e) Immunocytochemistry of endogenous Runx1, Sox5, Sox6, and Sox9 in human articular chondrocytes were detected by secondary antibodies with red and green fluorescence, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm.