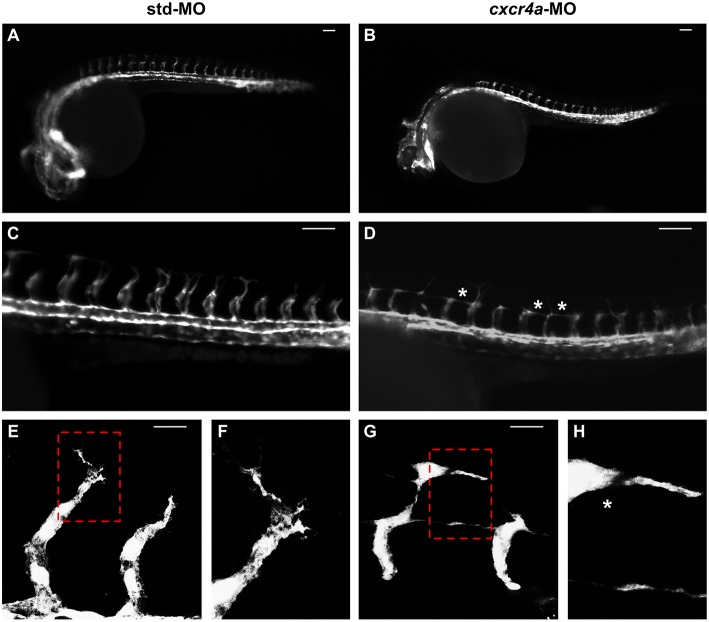
Figure 8.
cxcr4a knockdown affects ISV patterning. Tg(kdrl:EGFP) embryos injected with std-MO (A,C,E,F) or cxcr4a-MO (B,D,G,H) were photographed at 26 hpf under an epifluorescence microscope. (C,D) Extended focus of z-stacks images representing high magnification of the trunk region. Asterisk in (D) indicates aberrant ISV branching in cxcr4a-MO-injected embryos. (E–H) Confocal microscopy analysis of 28 hpf Tg(kdrl:EGFP) zebrafish embryos injected with std-MO (E,F) or cxcr4a-MO (G,H). Control embryos show filopodia protrusions emerging from sprouting ISVs (E). At variance, filopodia protrusions are strongly reduced or absent in cxcr4a morphants (asterisk in H) despite ectopic ISV branching (G). High magnification of the regions highlighted by dotted boxes are shown in (E,G), respectively. (A–D) Scale bar: 100 μm. (E–G) Scale bar: 25 μm.