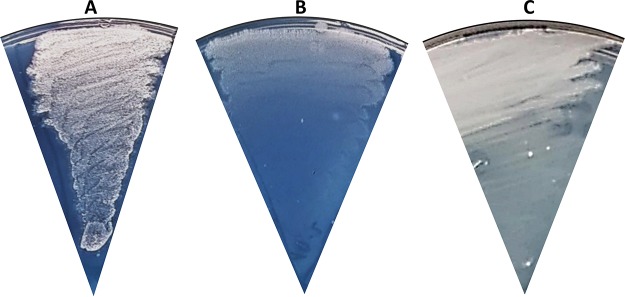
FIG 3.
Physiological role of the glnA4 gene product in S. coelicolor M145 cells grown in the presence of ethanolamine. Phenotypic analysis of S. coelicolor M145 (A), the ΔglnA4 mutant (B), and the complemented mutant ΔglnA4pRM4glnA4 (C) was performed on defined Evans medium with ethanolamine hydrochloride (25 mM) (A) as the sole nitrogen source. Deletion of the glnA4 gene resulted in compromised growth on ethanolamine, whereas complementation with pRMglnA4 under the control of its native promoter restored growth on ethanolamine.