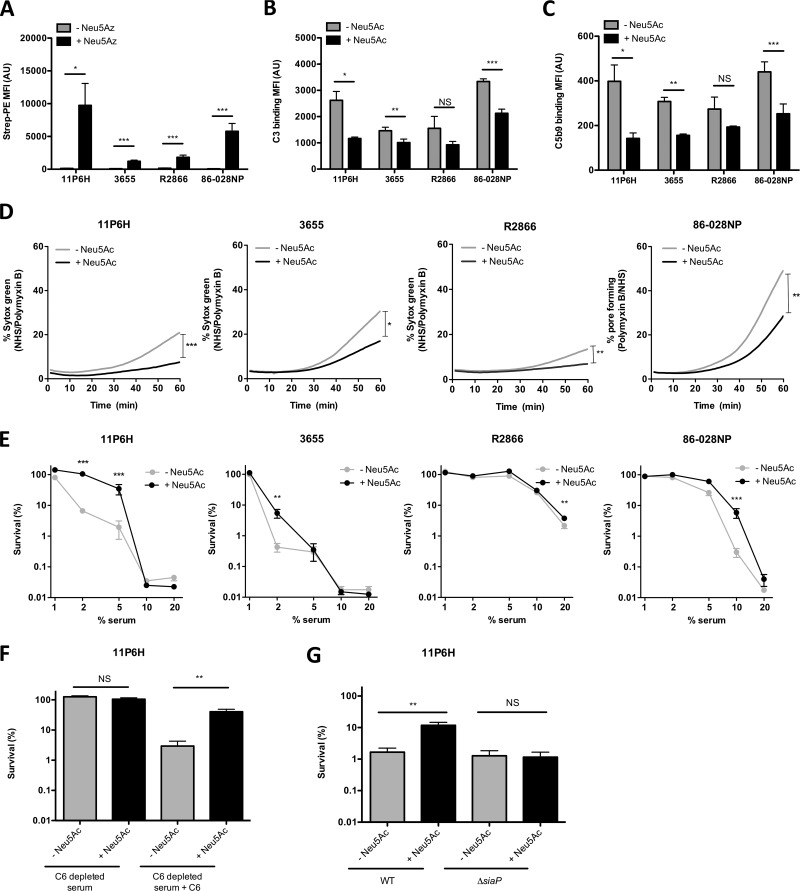
FIG 1.
Uptake of sialic acid decreases complement binding and serum killing of multiple NTHi strains. (A) Bacteria were grown with 100 μM Neu5Az, and the presence of Neu5Az on the bacterial surface was detected by flow cytometry (n = 6). Bacteria were incubated with 10% NHS in HBSS3+ for 30 min, and surface binding of complements C3 (B) and C5b9 (C) was determined by flow cytometry (n = 4). (D) Bacteria were incubated with 10% NHS, 10% HI serum, or 200 μg/ml polymyxin B in HBSS3+, and Sytox green signal was detected over a period of 60 min. Relative fluorescence intensity was determined by subtracting the fluorescence intensity of the NHS from the fluorescence intensity of the HI serum, followed by dividing it by the maximum fluorescence intensity of polymyxin B. The area under the curve was determined for statistical analysis (n = 4 or 6). (E) Bacteria were incubated with diluted NHS or diluted HI serum in HBSS3+ for 1 h, and survival was determined by dividing the CFU counts in NHS by the CFU count in HI serum after 1 h of incubation (n = 4). (F) NTHi 11P6H bacteria were incubated with 2.5% C6-depleted serum or 2.5% HI-C6-depleted serum in HBSS3+ for 1 h, and survival was determined by dividing the CFU counts in C6-depleted serum by the CFU count in HI-C6-depleted serum after 1 h of incubation (n = 6). (G) NTHi 11P6H WT or 11P6HΔsiaP mutant bacteria were incubated with 5% NHS or 5% HI serum in HBSS3+ for 1 h, and survival was determined by dividing the CFU counts in NHS by the CFU count in HI serum after 1 h of incubation (n = 3). A two-tailed paired t test (A, B, C, D, F, and G) or 2-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni posttest (E) was used for statistical analysis. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; NS, not significant.