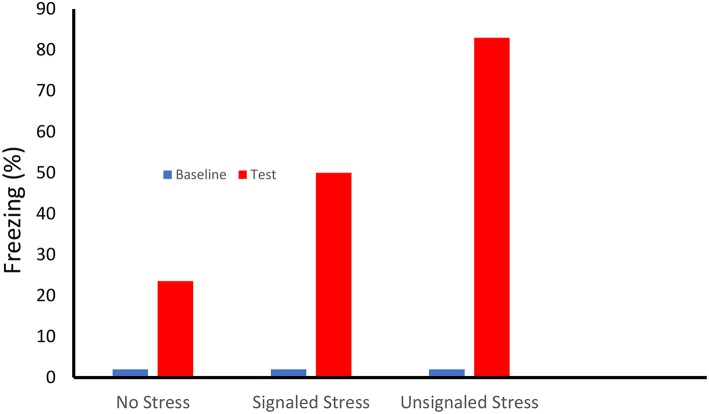
Figure 1.
On Day One female Long-Evans rats received either no treatment, or 15 shocks (0.71-mA, 0.75-s) that were either preceded by a 30 s tone (Signaled Stress) or followed by the tone (Unsignaled Stress) in a rectangular shuttle box. Subsequently the rats received a single conditioning shock (1.0-mA, 0.75-s) in a conditioning chamber that differed in term of shape, smell, location, dimensions and lighting. Prior to the conditioning shock the there was little freezing (< 2%) in the conditioning chamber. Animals that received a prior signaled shock stressor showed more than twice the level of freezing of the unstressed controls. Fear learning showed an even greater enhancement in that rats whose stress was unsignaled [Based on Fanselow and Bolles (1979a,b)].