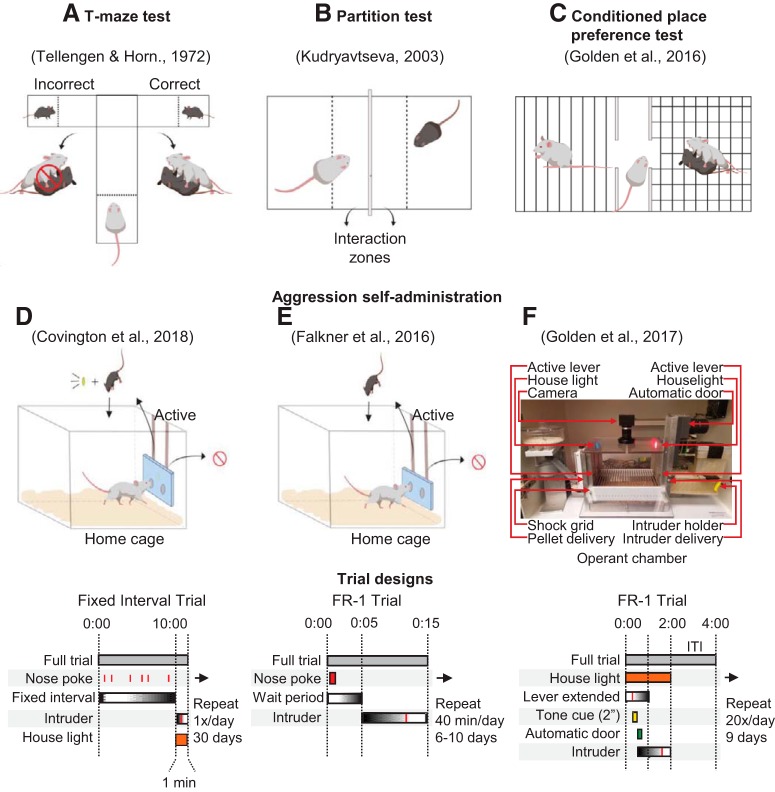
Figure 2.
Schematics of different behavioral procedures to study motivated aggression seeking behavior. A, In the T-maze test, dominant mice undergo preliminary aggressive experiences with a subordinate in their homecage. On test day, they are placed at the end of the long arm of the T-maze in a start box. At the ends of the short arms are “correct” or “incorrect” goal boxes. A subordinate mouse is placed at each end of the goal boxes and separated by a partition. Upon choosing the “correct” goal box, the partition separating the subordinate mouse is raised and the dominant mouse can engage in attack. Upon choosing the “incorrect” goal box, the subordinate mouse is removed before the partition is raised, eliminating the possibility of attack. B, In the partition test, the behavior of a dominant mouse is assessed when a subordinate mouse is placed at the opposite end of a box separated by a partition. The partition allows for all forms of sensory contact with the subordinate mouse, except for tactile contact. Approach behaviors and time spent in the “interaction zone” are recorded. C, In the CPP test, dominant mice are conditioned to two different contextual chambers, with one chamber paired to the presence of a subordinate mouse and the other chamber serving as an unpaired control. On test day, dominant mice are placed in a middle chamber connecting both contextual chambers. Time spent in the paired chamber compared with the unpaired chamber is measured. D, Operant approach used by Covington et al. (2018). A nose-poke apparatus is inserted into the dominant mouse's homecage. Nose-pokes in the active port are reinforced on a fixed-interval schedule (FI) with presentation of an intruder mouse into the homecage. An aggression-paired houselight illuminates upon insertion of an intruder. The other port serves as an inactive control. Bottom, A schematic of the FI trial design. E, Operant approach used by Falkner et al. (2016). As in D, a noseport panel containing two ports with infrared detectors is inserted into the dominant mouse's homecage. However, nose-pokes in the active port are reinforced on a fixed ratio-1 (FR-1) reinforcement schedule. Bottom, A schematic of the FR-1 trial design. F, Operant approach used by Golden et al. (2017a). Behavior is assessed in an operant chamber with an active and inactive lever. Active lever presses are reinforced on an FR-1 reinforcement schedule. A successful lever press results in sounding of a discriminative tone and opening of an automated guillotine door housing an intruder on the opposite side. An intruder is then guided into the operant chamber. Bottom, A schematic of the trial design. F, Adapted from Golden et al. (2017a).