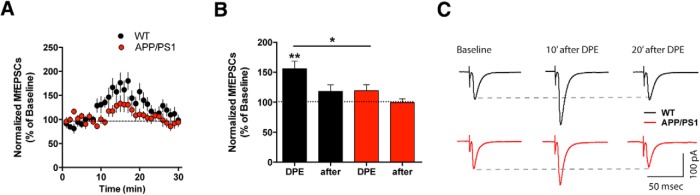
Figure 4.
Short-term synaptic plasticity dependent on membrane lipids is strongly reduced at Mf synapses of APP/PS1 mice. A, Summary time course of DPE experiments for WT (n = 10, 7 mice) and APP/PS1 (n = 12, 8 mice). The DPE protocol consists of a depolarization step from −70 to −10 mV for 9 s. B, Graph summarizing the increase in Mf-EPSCs amplitude after DPE. Values are normalized to the amplitude during the baseline period and data represented as mean ± SEM. There is an increase in the amplitude of Mf-EPSCs, which is significant in WT mice (single t test compared with baseline, p = 0.0016), but not in the APP/PS1 mice (p = 0.0747). C, Sample traces for Mf-EPSCs recorded during baseline (average of 40 sweeps), 5–10 min after DPE (30 sweeps), and 15–20 min after DPE (30 sweeps). All data represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.