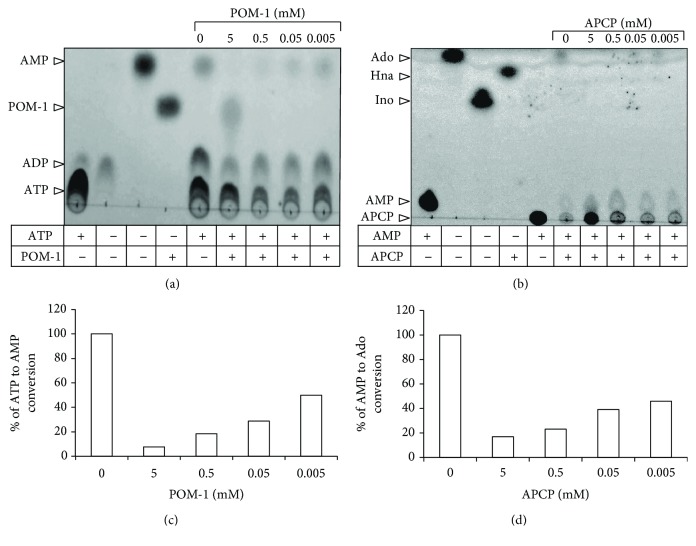
Figure 5.
Effect of POM-1 and APCP to inhibit the capacity of supernatants of cervical samples from patients with CIN-1 HPV-16+ to hydrolyze ATP or AMP. Aliquots of 2 μg of total protein obtained from the supernatants of cervical samples from patients with CIN-1 HPV-16+ were incubated in the presence of 5 mM of ATP or AMP and in the presence or absence of (5 mM, 0.5 mM, 0.05 mM, and 0.005 mM) of POM-I or APCP, specific inhibitors of CD39 and CD73, respectively. After 72 h of incubation, the ATP to AMP (a) and AMP to Ado (b) conversions were detected by TLC. The percentages of ATP to AMP (c) and AMP to Ado (d) conversions in the presence of several concentrations of POM-1 or APCP were determined by densitometric analysis in relation to the respective basal conversion (in the absence of the inhibitors), which was considered 100%. A representative assay from three independent experiments is shown.