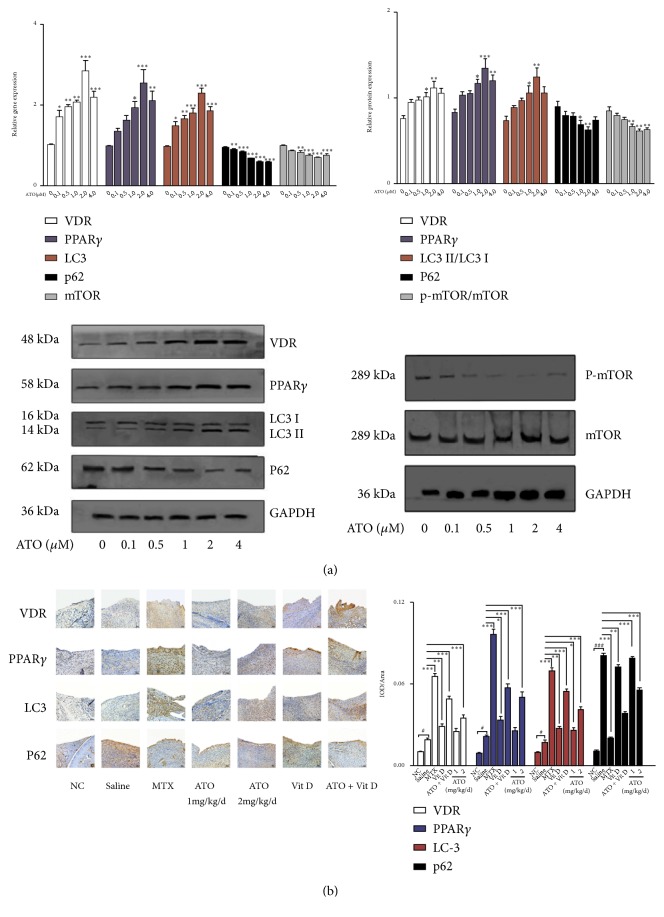
Figure 2.
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) and Vitamin D rescue the defective Vitamin D receptor (VDR)-PPAR-γ autophagy functional module in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). (a) Increased expression levels of PPAR-γ, VDR, and LC-3 and decreased expression levels of p62 after ATO administration in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) (n=3; ∗p<0.05; ∗∗p<0.01). Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (b) Increased average integrated optical density (IOD) values for VDR, PPAR-γ, LC-3, and p62 in synovial tissue in collagen-induced arthritis- (CIA-) saline mice (saline) compared with normal controls (NC). CIA mice under ATO and methotrexate (MTX) treatments showed additional increased average IOD values for VDR, PPAR-γ, and LC-3 but decreased p62 in synovial tissue compared with the saline group (n=6; ∗p<0.05; ∗∗p<0.01; ∗∗∗p<0.001, experiment versus saline). Magnification = 20×. Bars = 50 μm. Data are expressed as means ± SEM.