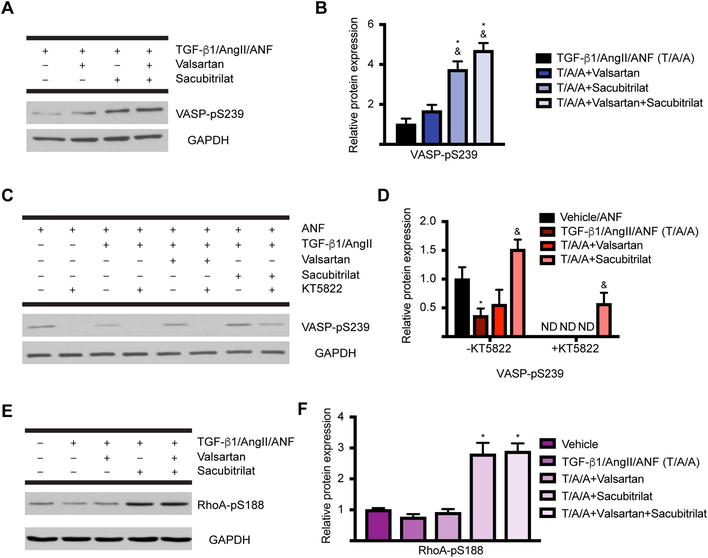
Figure 6: Sacubitrilat stabilizes PKG signaling and inhibits RhoA in activated CF.
A. Sacubitrilat alone or in combination with valsartan promotes the PKG-dependent phosphorylation of VASP at S239. B. Quantification of (A). n = 3 for each condition for all experiments. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. * = p < 0.05 relative to TGF-β1/AngII/ANF, & = p < 0.05 relative to TGF-β1/AngII/valsartan. C. Use of the PKG inhibitor KT5822 confirms that Sacubitrilat effects are transduced primarily through PKG. D. Quantification of (C). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. * = p < 0.05 relative to vehicle/ANF, & = p < 0.05 relative to TGF-β1/AngII/ANF; ND, not detected. E. Sacubitrilat promotes the PKG-dependent phosphorylation of RhoA at S188, which inactivates RhoA (a major transducer of myofibroblast activation). F. Quantification of (E). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. * = p < 0.05 compared to vehicle.