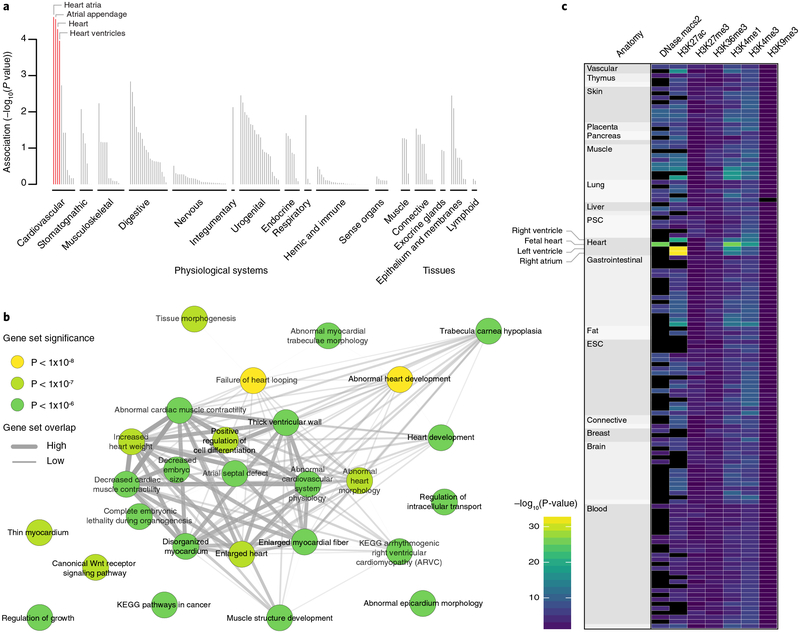
Fig. 2 |. Tissues, reconstituted gene sets, and regulatory elements implicated in atrial fibrillation.
a, Based on expression patterns across 37,427 human mRNA microarrays, DEPICT predicted genes within atrial fibrillation-associated loci to be highly expressed across various cardiac tissues. Tissues are grouped by type and significance. Red columns represent statistically significant tissues following Bonferroni correction (P< 0.05/209 = 0.0002). b, Top (P< 1× 10−6) reconstituted gene sets (out of 826 with FDR < 0.05 and after exclusion of ‘gene subnetworks’) found by DEPICT to be significantly enriched for genes in atrial fibrillation-associated loci. Each node, colored according to the permutation P value, represents a gene set and the gray connecting lines represent pairwise overlap of genes within the gene sets. c, Heatmap indicating the overlap between atrial fibrillation-associated risk variants and regulatory elements across 127 Roadmap Epigenomics tissues (each represented by a row) using GREGOR. Black indicates no data. PSC, pluripotent stem cell; ESC, embryonic stem cell.