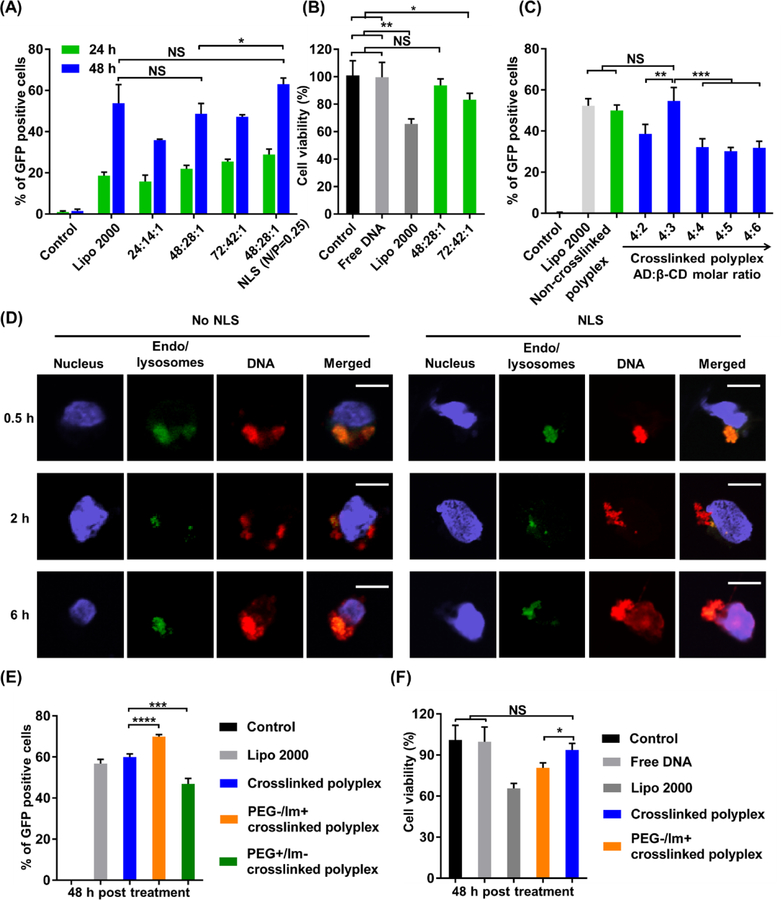
Figure 4. Efficient delivery of plasmid DNA by the polyplexes.
(A) The effects of polyplex formulation on the DNA transfection efficiency of polyplexes. Cells were treated with Lipo 2000, non-crosslinked polyplexes with three different PBAP:PEG–PBAP–PEG: DNA weight ratios, as well as the polyplex with a PBAP:PEG–PBAP–PEG: DNA weight ratio of 48:28:1 together with NLS (N/P ratio = 0.25). (B) Effects of polyplex formulation on the cytotoxicity of non-crosslinked DNA polyplexes with different weight ratios. (C) Optimization of the AD:β-CD molar ratio in crosslinked CLPBAP polyplexes. HEK 293 cells were treated with Lipo 2000, non-crosslinked PBAP polyplexes, and crosslinked CLPBAP polyplexes with different crosslinker molar ratios. The transfection efficiency was measured 48 h post treatment. (D) Intracellular trafficking of the crosslinked DNA polyplex with and without NLS. Scale bar: 10 μm. (E-F) Effects of PEG and imidazole groups on the transfection efficiency of the crosslinked polyplexes. (E) Transfection efficiency of PEG- or imidazole-lacking crosslinked polyplexes. (F) Cell viability of PEG-lacking crosslinked polyplexes. NS: not significant; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ****: p < 0.0001; n = 3.