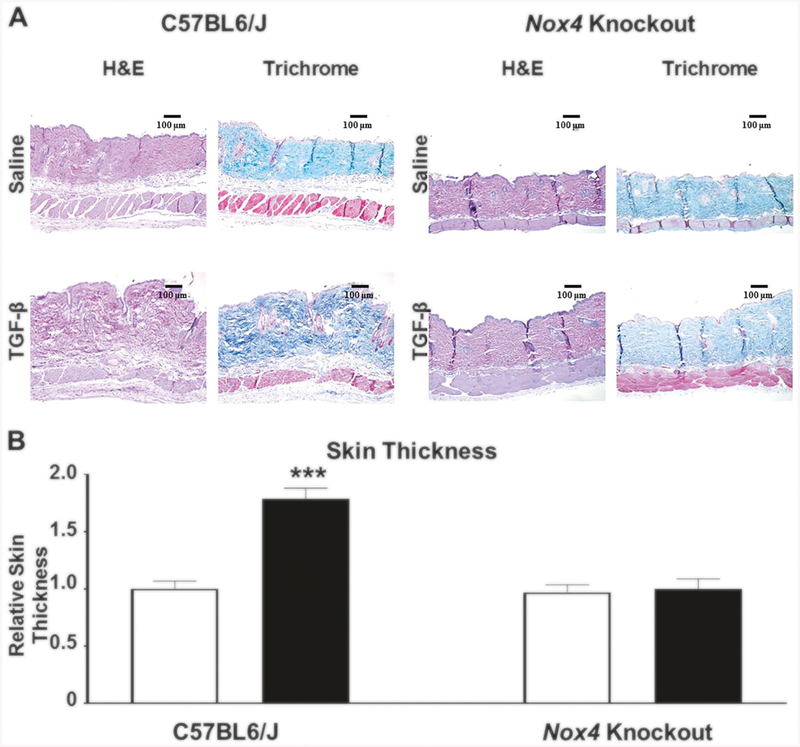
Fig. 1.
a Histopathology of skin from male C57BL6/J and Nox4 knockout mice implanted with subcutaneous osmotic pumps containing either saline or TGF-β1. Representative sections of skin tissues isolated from male C57BL6/J control mice (left panels) and B6.129-Nox4tm1Kkr/J (Nox4 knockout) mice (right panels) implanted with subcutaneous pumps containing either saline (upper rows) or 2.5 μg TGF-β1 (lower rows) stained with H&E or Masson’s trichrome. TGF-β1-treated male C57BL6/J mice display increased dermal thickness and collagen accumulation compared to saline-treated controls. The induction of a fibrotic response following treatment with TGF-β1 was abrogated in skin samples isolated from Nox4 knockout mice. b Relative thickness of skin from male C57BL6/J and Nox4 knockout mice implanted with subcutaneous osmotic pumps containing either saline or TGF-β1. The shortest distance between the epidermal–dermal junction and the dermal–adipose layer junction was measured at five randomly selected fields from one sample from each animal. The results were normalized to the mean skin thickness in saline-treated C57BL6/J control mice and represent the mean relative thickness ± SD of five measurements per mouse in each experimental group