Fig. 7. Catalytic scheme of TmPPase and its inhibition by ATC.
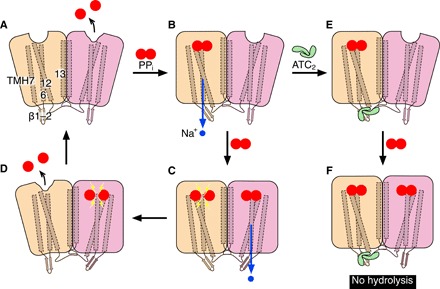
(A) The binding of the substrate (PPi; two joined red circles) to monomer A (wheat color) leads to Na+ pumping (blue circle and blue arrow for the pumping direction) and induces a conformational change in monomer B (pink color). (B) This change increases the affinity of monomer B for the substrate. The Na+ pumping causes substrate hydrolysis (yellow lightning symbol for this event) in monomer A, while the substrate binding in monomer B leads to its Na+ pumping (C). (D) After hydrolysis, monomer A releases its hydrolysis products (2Pi; red circles), while monomer B proceeds to the hydrolysis event, returning the enzyme to state A. The ATC dimer binds to its binding site after substrate binding and Na+ pumping in monomer A (E), which locks this monomer in the “down” state. Although no hydrolysis can occur in monomer A due to the ATC binding, the conformational change may still induce a conformational change in monomer B, which increases its affinity for the substrate (F). The numbering with white background corresponds to TMH number.
