Fig. 6. Neural circuits of bristle MSN–driven labellar spread.
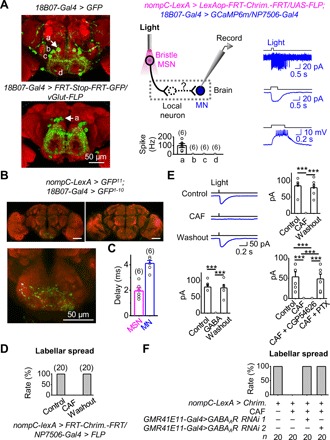
(A) Patch-clamp recordings of GMR18B07 MNs. Left: SEZ neurons labeled by GMR18B07-Gal4 (top) and four pairs of SEZ MNs labeled by intersection with vGlut-FLP and GMR18B07-Gal4 (bottom). a, b, c, and d mark the four pairs of MNs. Middle: Illustration of simultaneous optogenetic activation and patch-clamp recordings (top); collective data (bottom). Right: Electrical responses of GMR18B07 MNs under cell-attached recordings (top), voltage-clamped in perforated patch-clamp recordings (middle), and current-clamped in perforated patch-clamp recordings (bottom). (B) GRASP between labellar MSNs and GMR18B07 neurons. Top: GRASP signal between labellar MSNs and GMR18B07 neurons (left); no GRASP signal in the absence of GMR18B07 driver (right). Bottom: GRASP signal in the SEZ (expanded from top left panel). (C) Monosynaptic connections between bristle MSNs and GMR18B07 MNs. Collective data of synaptic delay from bristle MSNs to GMR18B07 MNs (n = 6). Light stimulation: 2 ms, 617 nm. (D) Bitter GRNs inhibit bristle MSN–driven labellar spread. CAF, 50 mM. (E) Bitter GRNs inhibit bristle MSN–driven responses of GMR18B07 MNs. Top: Bristle MSN–driven responses of GMR18B07 MNs in Ringer, CAF, and after wash out CAF (left) and collective data (right). Bottom: Collective data of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) blockage of bristle MSN–driven responses of GMR18B07 MNs (left); GABAA receptor antagonist blocks inhibition of bristle MSN–driven responses of GMR18B07 MNs by bitter GRNs (right). CAF, 20 mM; GABA, 1 mM; CGP54626, 25 μM; PTX, 25 μM. ***P < 0.001. n = 6. (F) Knocking down GABAA receptor eliminates inhibition of bristle MSN–driven labellar spread by bitter GRNs.
