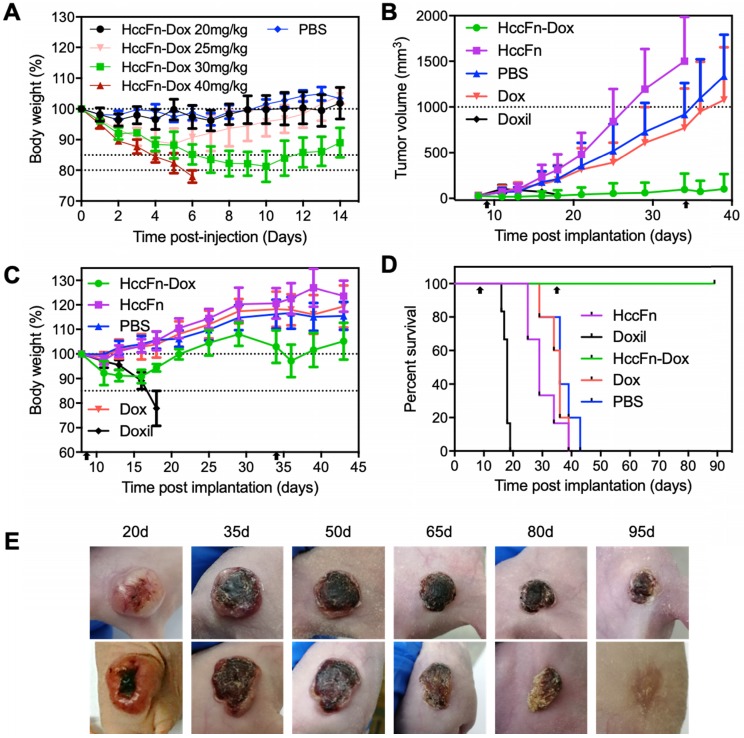
Figure 5.
HccFn-Dox nanocages effectively killed HCC tumor and exhibited less toxicity than Doxil. (A) Tolerability study of HccFn-Dox. HccFn-Dox at 20, 25, 30, or 40 mg/kg Dox equivalents were intravenously injected into healthy BALB/c mice (n=4 per group) on day 0, with PBS injection as control. Tumor growth (B), body weight change (C), survival time (D), and tumor cell morphology (E) for tumor-bearing mice upon injection of HccFn-Dox at 25 mg/kg Dox equivalents. HepG2 tumor cells were implanted subcutaneously into mice on day 0. Mice were intravenously administrated with HccFn-Dox (25 mg/kg Dox equivalents, n=6), and control substances such as Doxil (25 mg/kg Dox equivalents, n=6), Dox (5 mg/kg Dox equivalents, n=6), HccFn (60 mg/kg, n=6), or PBS (n=5) on day 9 and day 34. Black arrows indicated the administration time.