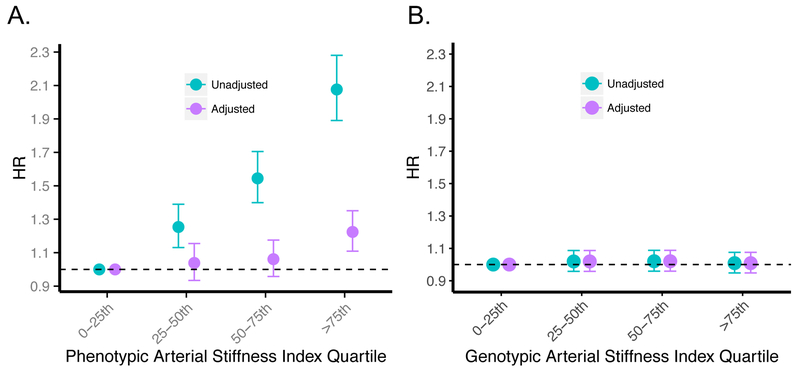
Figure 2: Epidemiologic and genetic associations of arterial stiffness index with incident coronary artery disease.
Association between (A) phenotypic ASI, and, (B) the ASI GRS, with incident coronary artery disease in the UK Biobank. Results are presented as both unadjusted (cyan) and adjusted (purple) by age, sex, smoking status, prevalent hypertension, prevalent hypercholesterolemia, prevalent diabetes, heart rate, vegetable intake, alcohol intake, and exercise frequency. For the ASI GRS instrument, analysis was performed excluding individuals used in the ASI genome-wide association study. Hazard ratios represent increased risk of incident CAD resulting from (A) 1 SD increase in ASI phenotype, and (B) 1 SD increase in genetically-mediated ASI from the ASI GRS. Sample sizes for (A) the phenotypic association are 3,692 cases, 126,615 controls, and for (B) the genotypic association are 7,534 cases, 215,527 controls.
ASI = Arterial stiffness index, CAD = coronary artery disease, GRS = genetic risk score, HR = hazard ratio, SD = standard deviation.