Figure 5. Zinc intoxication leads to ferroptosis in A549 cells.
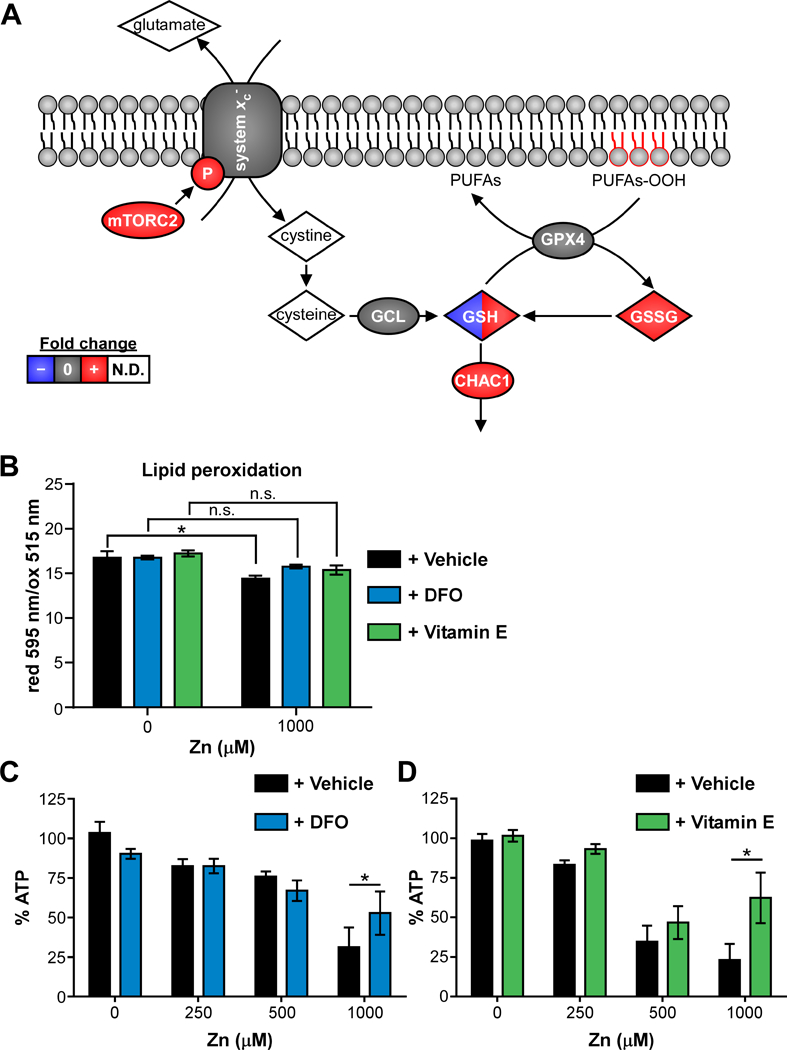
(A) Schematic of ferroptosis network is painted with results from multi-omics analysis. Species painted with two colors indicates time-dependent changes in fold-change. (B) Lipid peroxidation is significantly increased (lower reduced/oxidized) in A549 cells treated with 500 μM Zn, but not in the presence of desferoxamine (DFO, 100 μM) or α-tocopherol (Vitamin E, 100 μM). (C-D) Addition of DFO or vitamin E (100 μM) limits loss of viability at 24 h when A549 cells are intoxicated with 1000 μM Zn (% of 0 μM). Abbreviations: GSH: reduced glutathione; GSSG: oxidized glutathione; N.D.: not detected; PUFAs: polyunsaturated fatty acids; PUFAs-OOH: polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxides.
